-
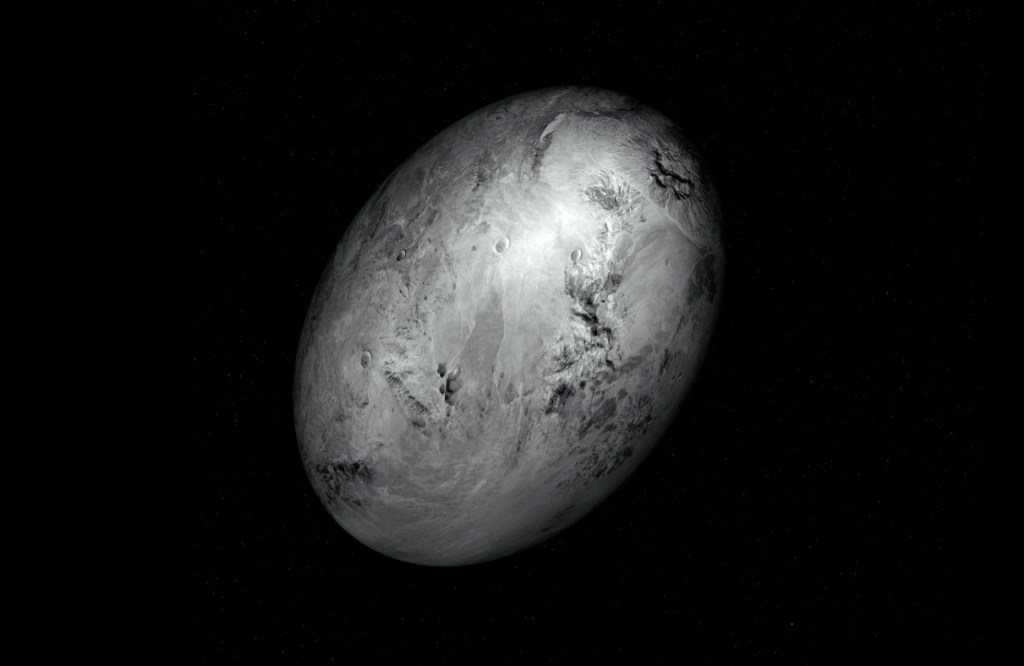

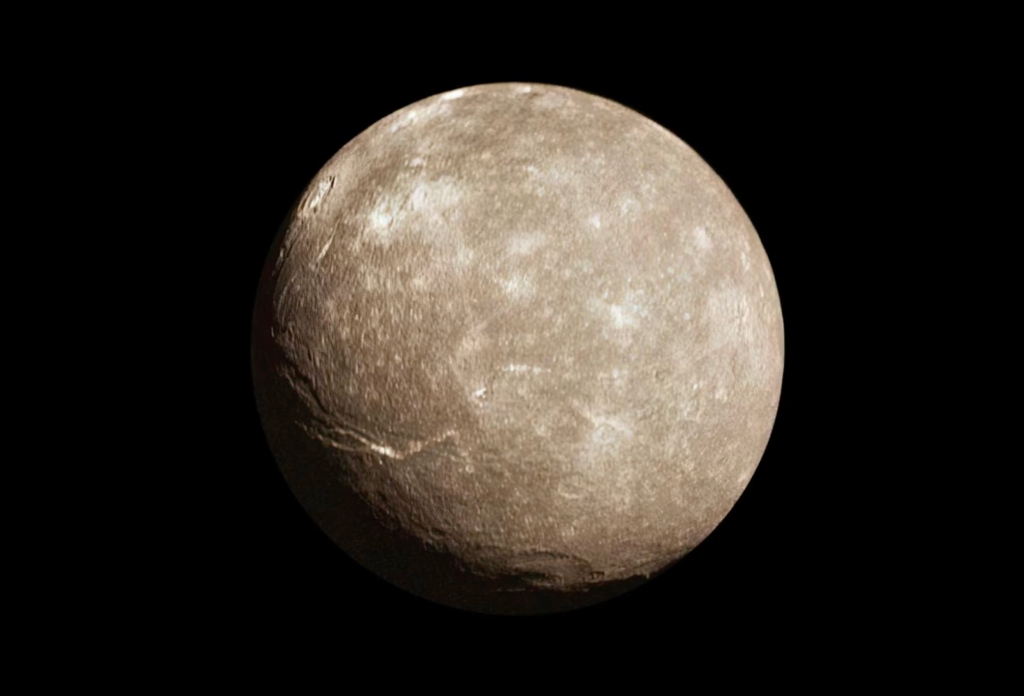
In a recent study, astronomers have advanced our understanding of the complex dynamics of the Haumea system, a dwarf planet located in the Kuiper Belt, beyond Neptune. Haumea is known for its rapid rotation, unique shape, and the presence of two moons, Hi’iaka and Namaka, along with a ring system and a family of spectrally…
-
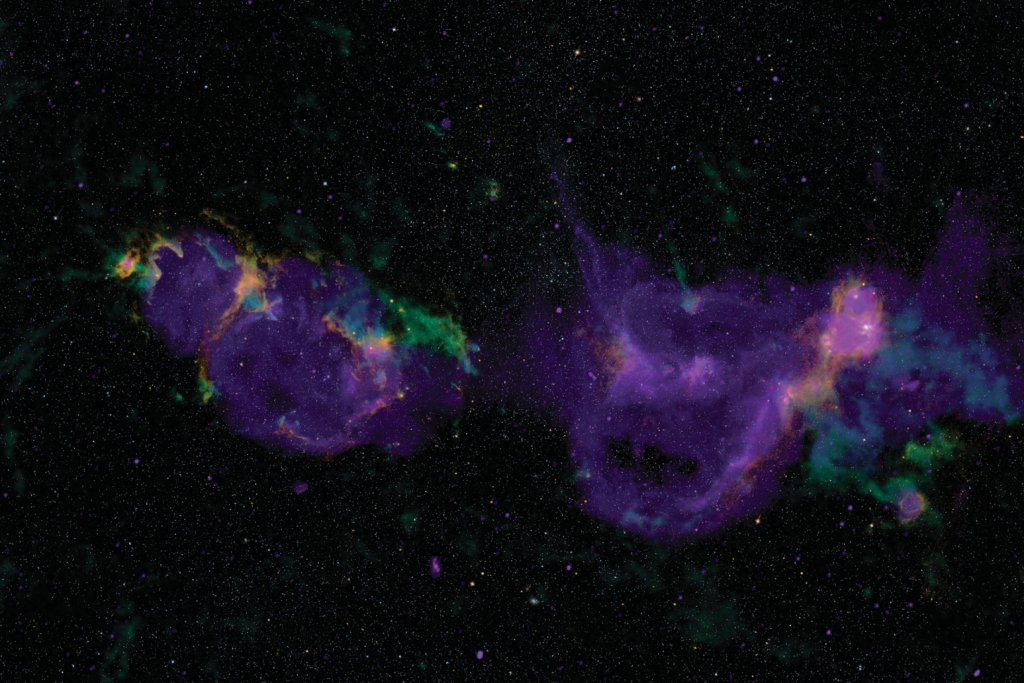
Astronomers have recently conducted an in-depth study of the W5-NW star-forming complex, uncovering clear signs that collisions between clouds of gas in space can trigger the birth of stars and even entire star clusters. This complex, part of the larger W3/W4/W5 molecular cloud system located in the Perseus spiral arm of the Milky Way, has…
-
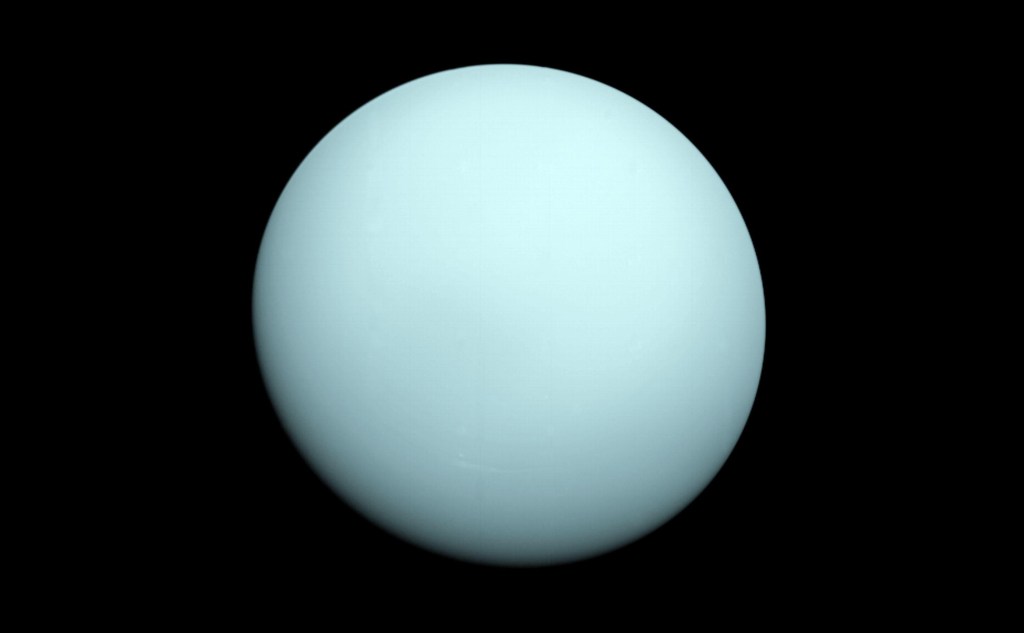

A new study of Uranus contributes to our understanding of planetary formation, with scientists asserting that the noble gases argon, krypton, and xenon could provide critical insights into the cosmic lineage of the distant ice giant. These inert gases, known for their lack of chemical reactivity and propensity to remain unchanged over eons, are now…
-
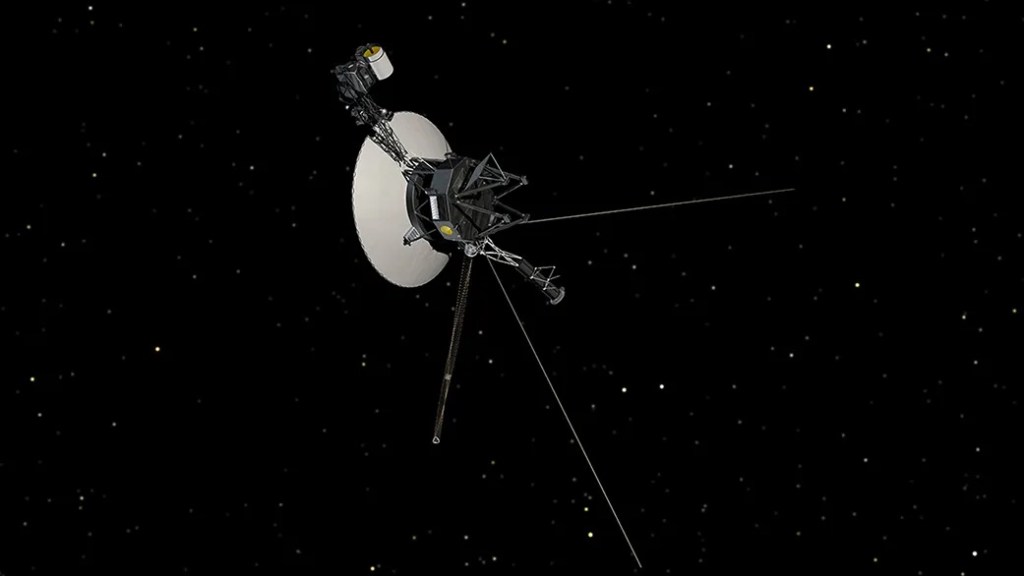

NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft, which entered the very local interstellar medium (VLISM) on August 25, 2012, followed by its twin, Voyager 2, on November 5, 2018, continue to unlock the mysteries of the cosmos beyond our solar system’s confines. These intrepid explorers, now traveling through the VLISM, have been transmitting invaluable data back to Earth,…
-
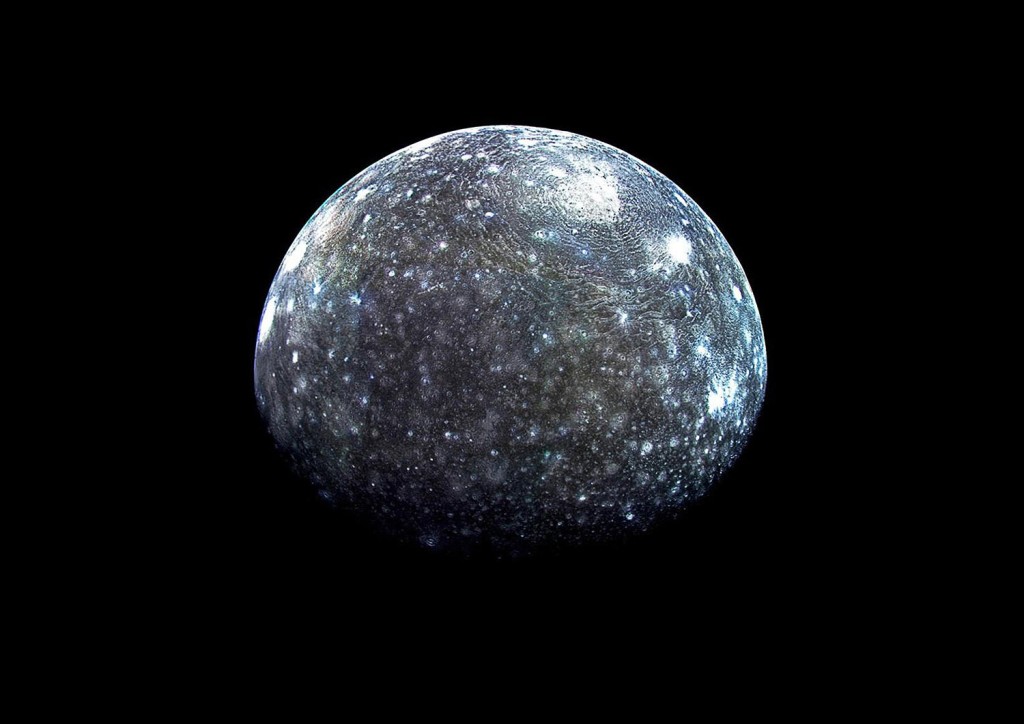

Utilizing the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), astronomers have unveiled new insights into the atmospheric composition of Callisto, one of Jupiter’s Galilean moons. The research, conducted with the NIRSpec Integrated Field Unit, has revealed the presence of carbon dioxide (CO2) gas across Callisto’s atmosphere, marking the first detection of CO2 gas over the moon’s trailing…
-
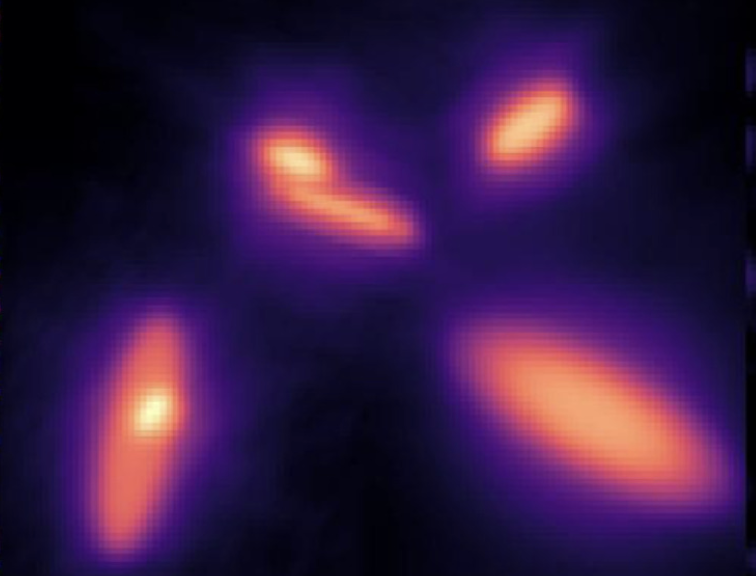

Astronomers have made a new discovery using the Hubble Space Telescope, shedding light on the origins of a Fast Radio Burst (FRB), dubbed FRB 20220610A, which has puzzled scientists since its detection in June 2022. This FRB, which has not been observed to repeat, hails from a galaxy with a redshift of z = 1.017,…
-
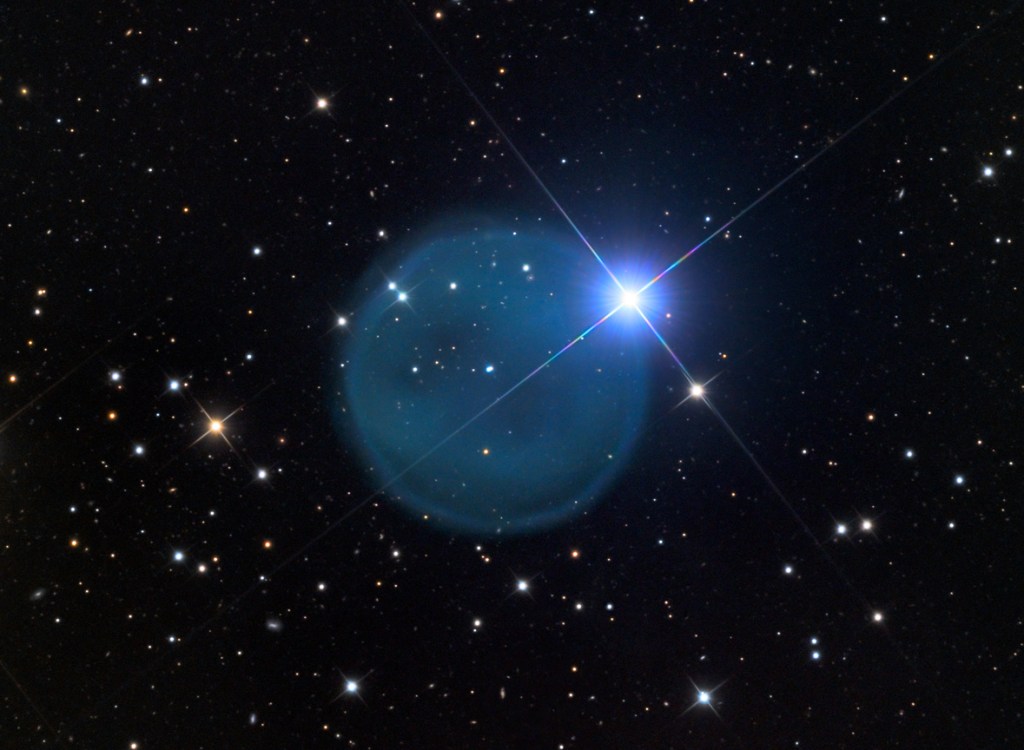

In an exciting development, researchers using the state-of-the-art Low-Resolution Spectrograph (LRS2) mounted on the 10-meter Hobby-Eberly Telescope (HET) at McDonald Observatory have identified three enigmatic stars nestled within faint planetary nebulae. These discoveries, part of a comprehensive spectroscopic survey aimed at unraveling the mysteries of faint Galactic planetary nebulae, mark a significant leap forward in…
-
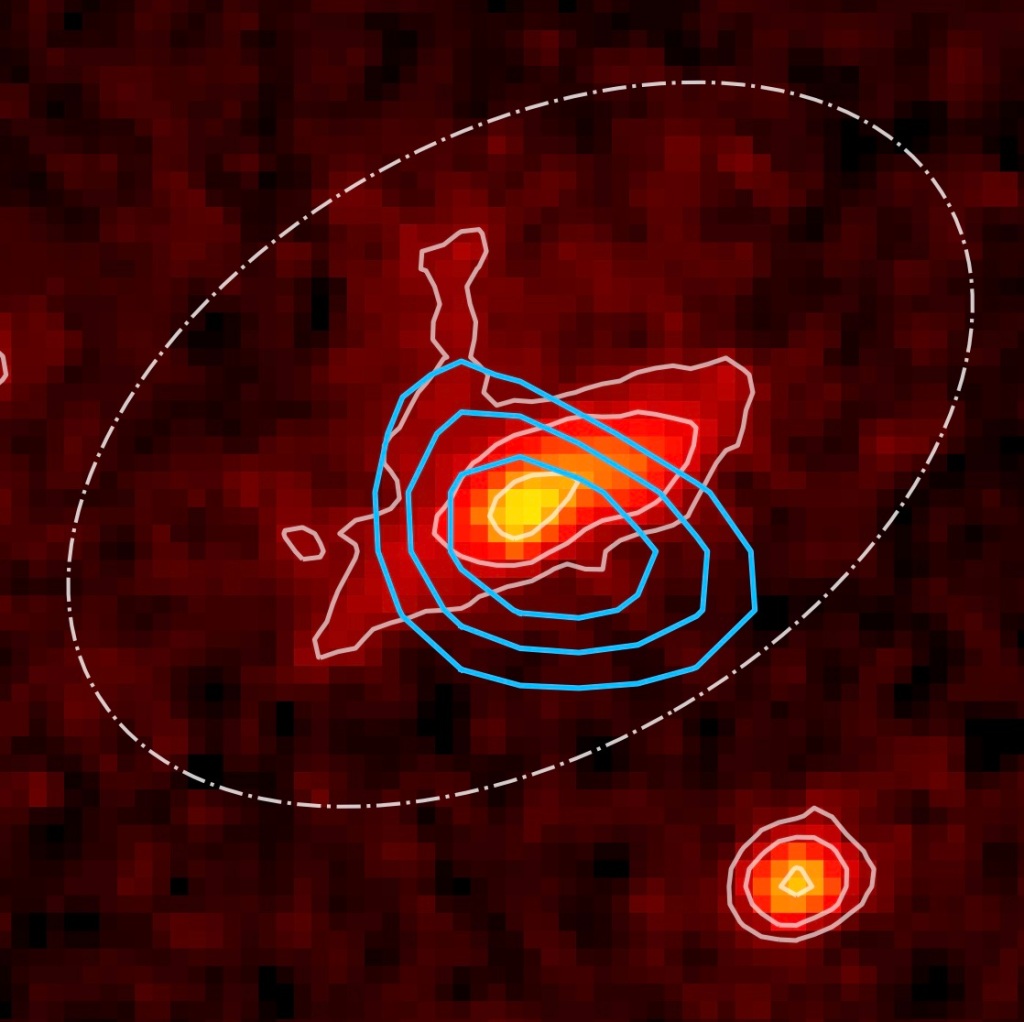
Researchers have utilized the unparalleled capabilities of the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) to conduct the first-ever spatially-resolved analysis of Dusty Star-Forming Galaxies (DSFGs) and a Lyman-break galaxy (LBG) located in a galactic conglomerate at the astonishing redshift of z = 4.05. These galaxies, situated in the densest corners of the universe, are renowned for…
-
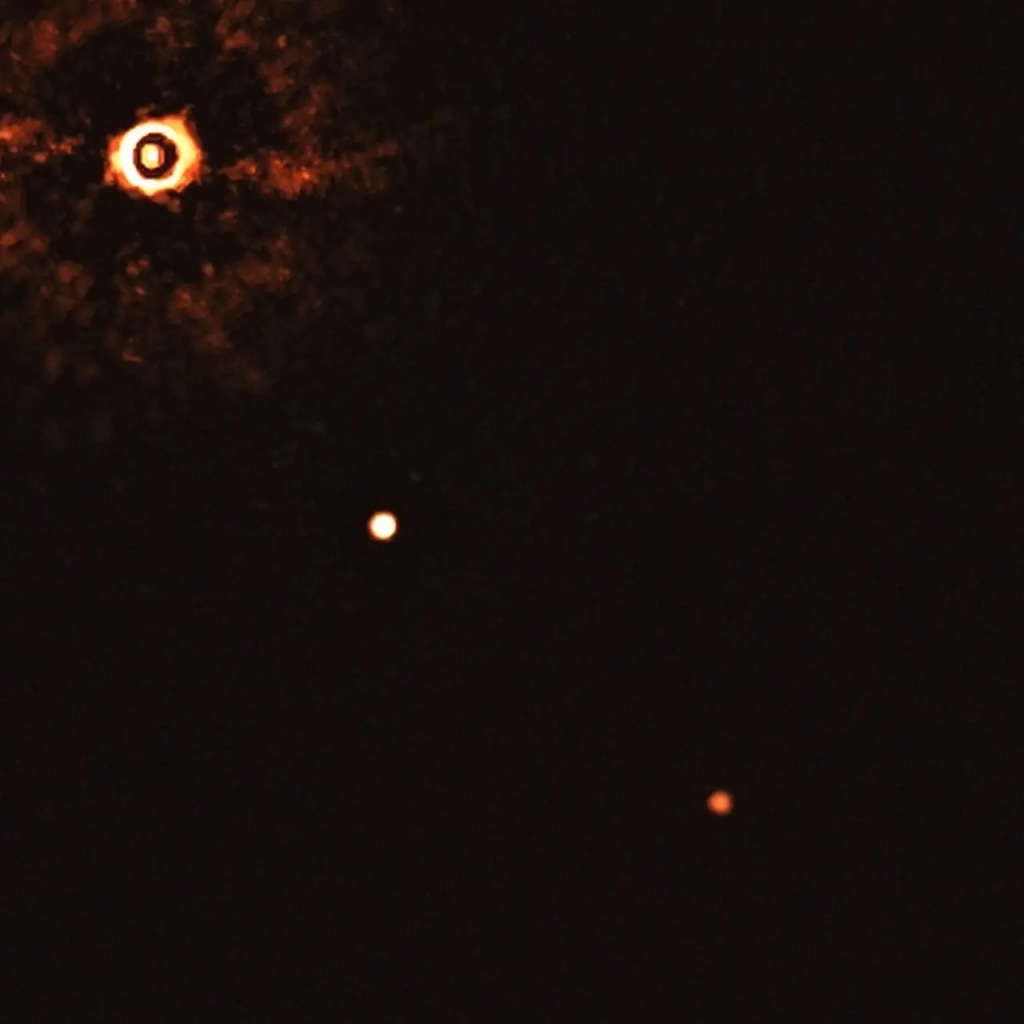

In a remarkable advancement in the quest to uncover the mysteries of distant worlds, a team of astronomers has introduced a groundbreaking machine-learning technique aimed at revolutionizing the detection of faint point sources within the vastness of space, particularly through high-contrast adaptive optics (AO) imaging data. This novel approach, which significantly boosts the sensitivity and…
-
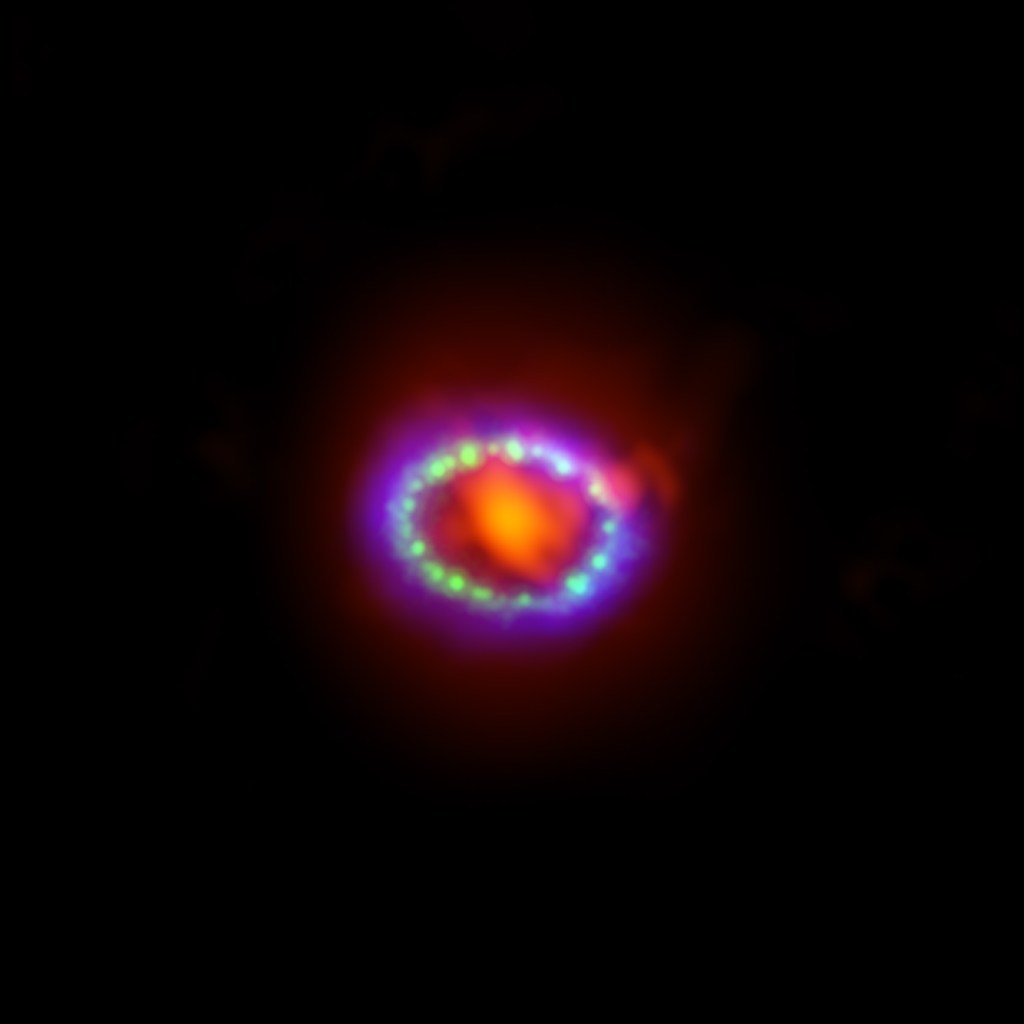
In a new and novel approach to the search for extraterrestrial intelligence (SETI), scientists have developed the “SETI Ellipsoid” strategy, which aims to detect signals from alien civilizations by focusing on technosignatures that may have been broadcast in synchronization with notable galactic events, such as supernova 1987A. This innovative method leverages the concept of a…
-
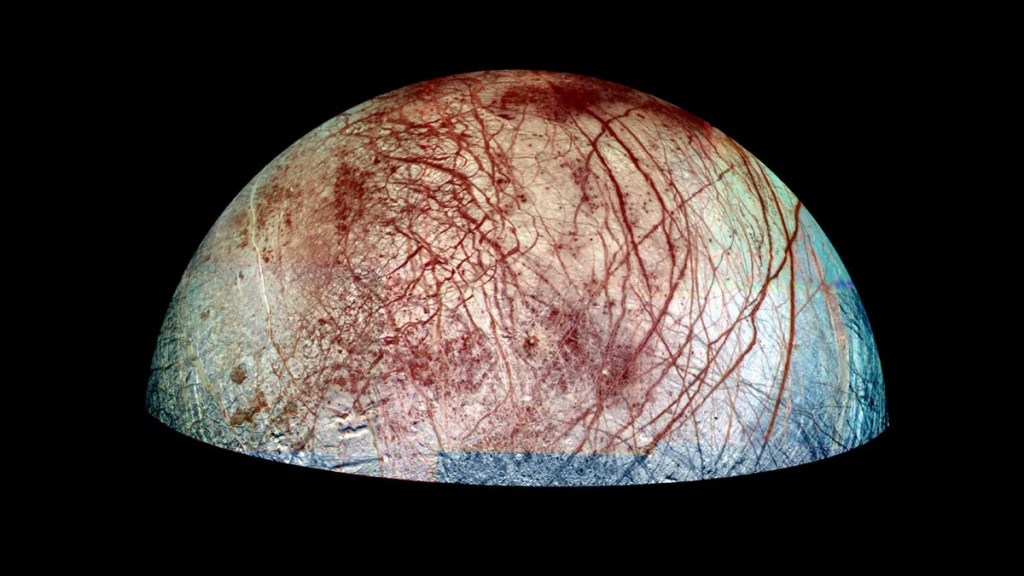
In a groundbreaking study focused on Jupiter’s moon Europa, scientists have delved into the mysteries lying beneath its icy exterior, revealing significant findings about its subsurface properties. Utilizing data from the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), the research team embarked on a detailed examination of Europa’s near-subsurface, spanning depths of approximately 1 to 20 centimeters.…
-
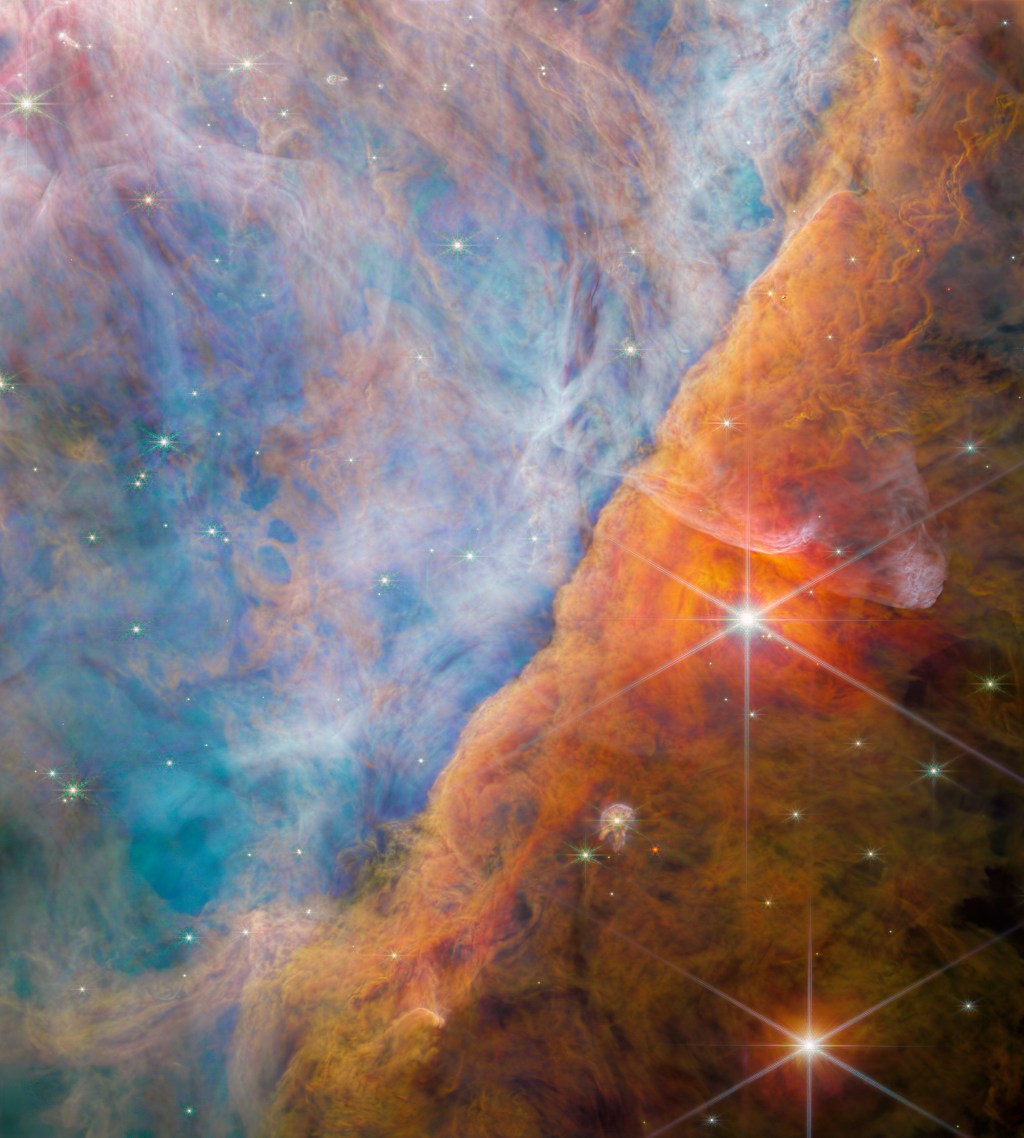

An international team of astronomers has utilized the unparalleled capabilities of the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) to carry out sophisticated 870 μm polarimetric observations across a sample of 61 protostars nestled within the vast expanse of the Orion molecular clouds. This ambitious study, boasting a resolution of approximately 400 astronomical units (AU)—equivalent to the…
-
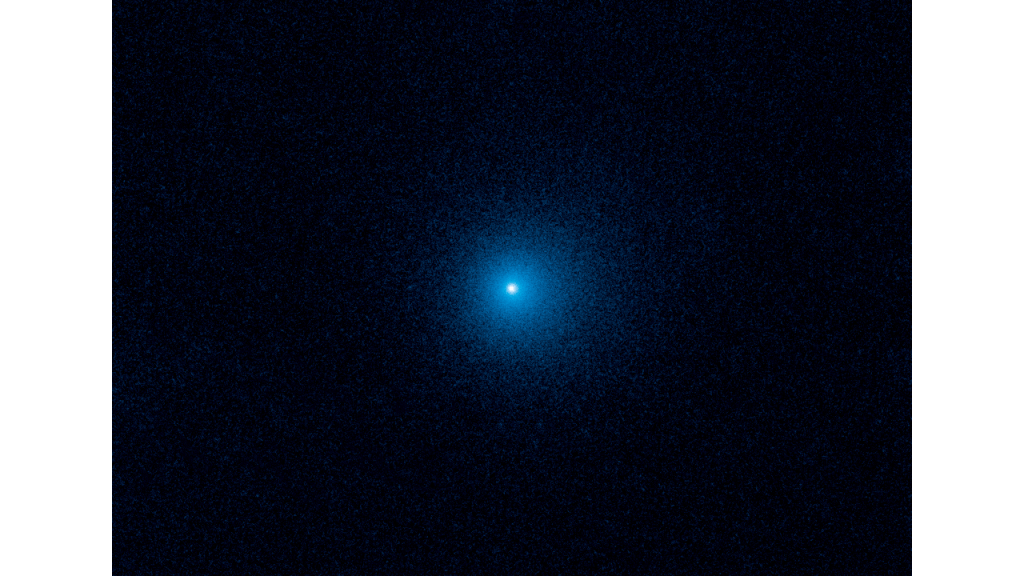

Scientists have announced the discovery of a new ultradistant comet, C/2019 E3 (ATLAS), marking it as the fourth comet of its kind to exhibit preperihelion activity at remarkable heliocentric distances of more than 20 astronomical units (AU). This discovery adds to the growing list of ultradistant comets, including C/2010 U3 (Boattini), C/2014 UN271 (Bernardinelli–Bernstein), and…
-
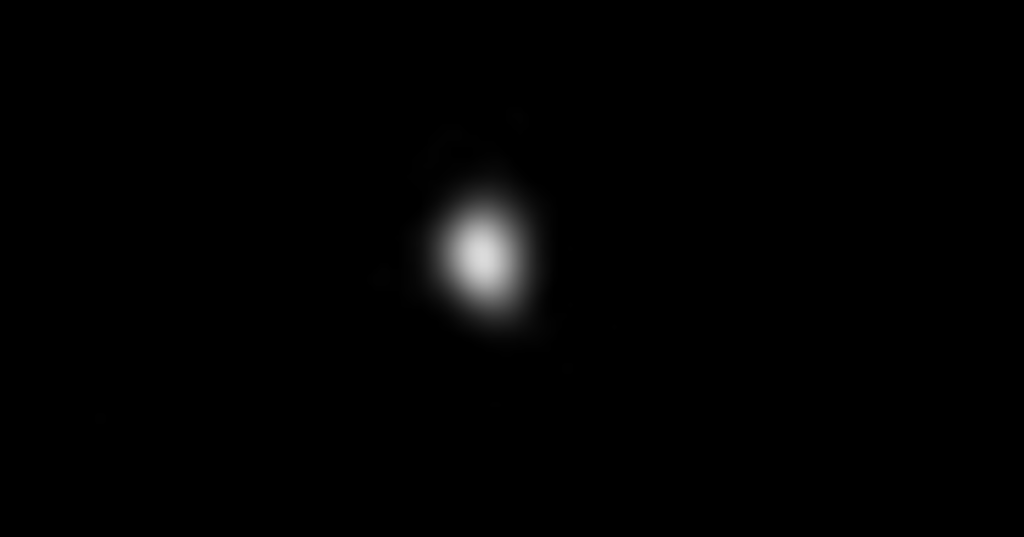

In an unprecedented exploratory effort that spanned the years 2006, 2009, and 2010, astronomers harnessed the capabilities of the MMT Observatory’s Red Channel spectrograph to delve into the mysteries surrounding Jupiter’s irregular satellites, including JVI Himalia, JVII Elara, JVIII Pasiphae, JIX Sinope, JX Lysithea, JXI Carme, JXII Ananke, and JXVII Callirrhoe. This comprehensive study, employing…
-
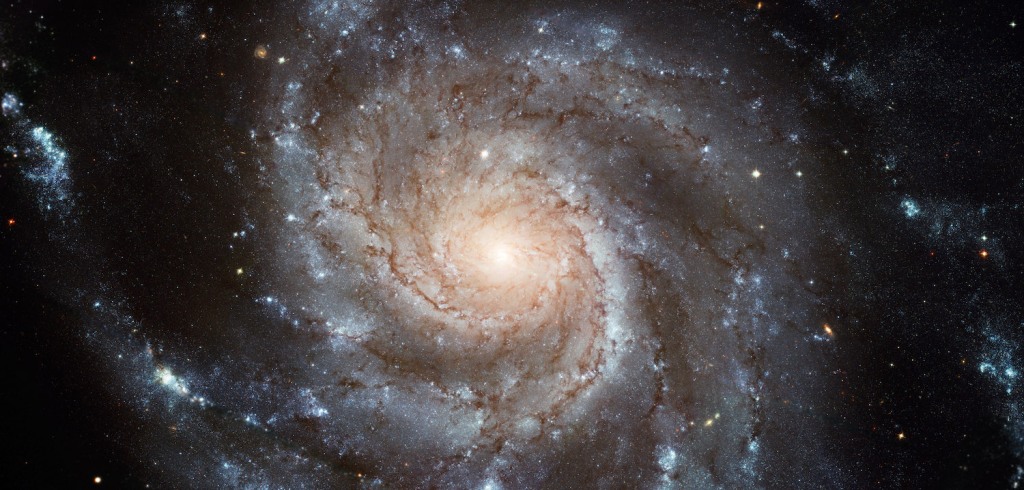

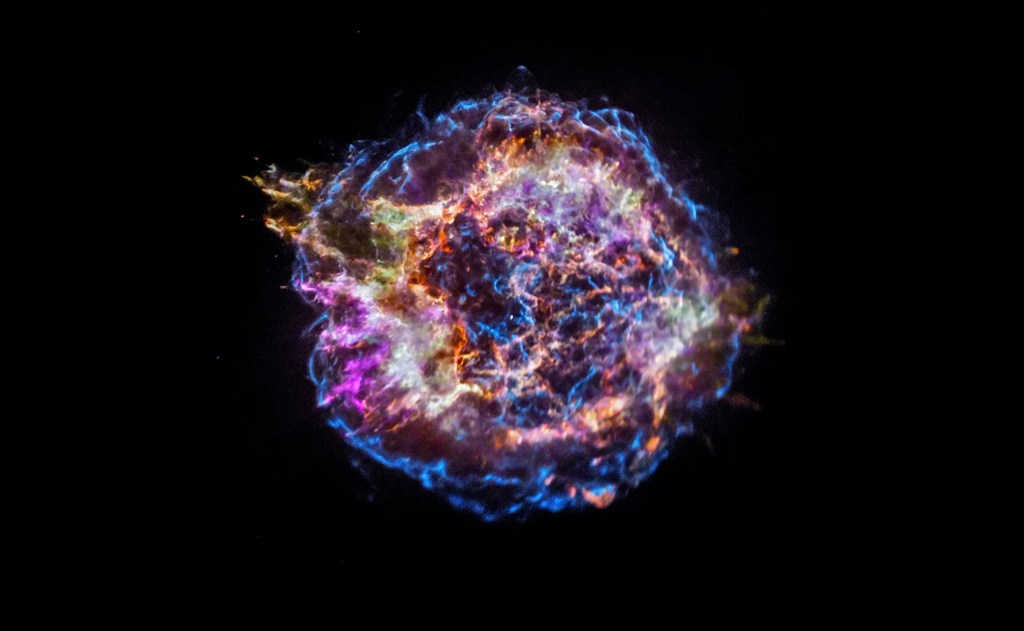
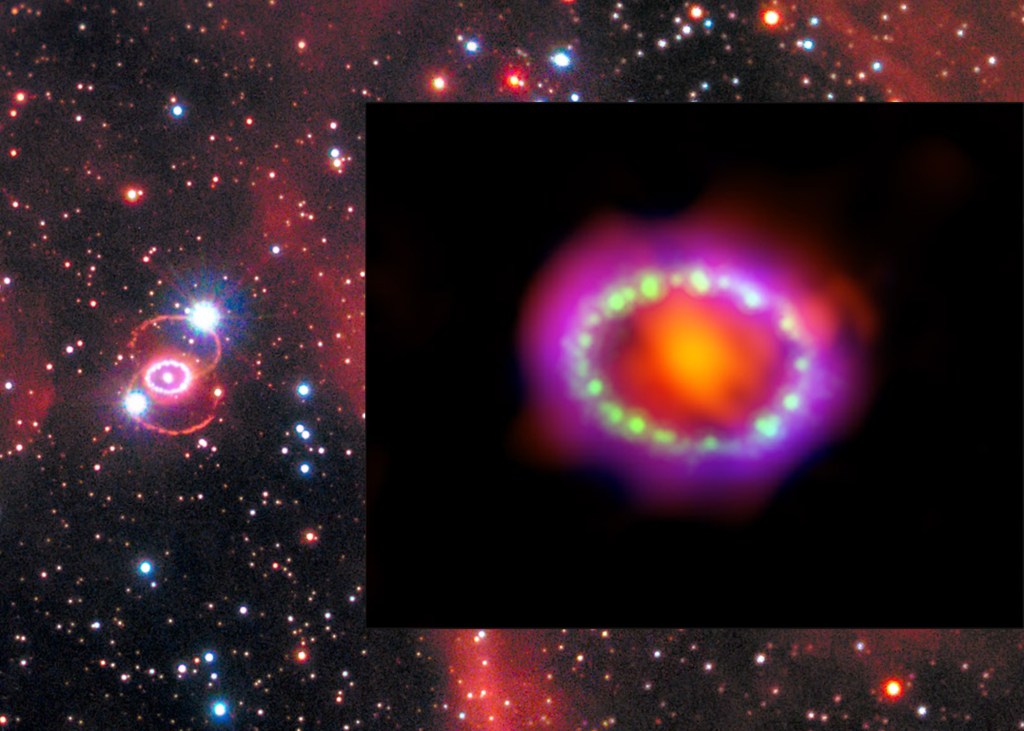
In an exciting development for the field of astrophysics, recent observations made with the Chandra Advanced CCD Imaging Spectrometer (ACIS) have provided unprecedented insights into Supernova 2023ixf, located in the nearby galaxy M101. Recorded on the 13th and 86th days following the explosion, these observations have pierced through the cosmic veil, revealing the intense interactions…
-
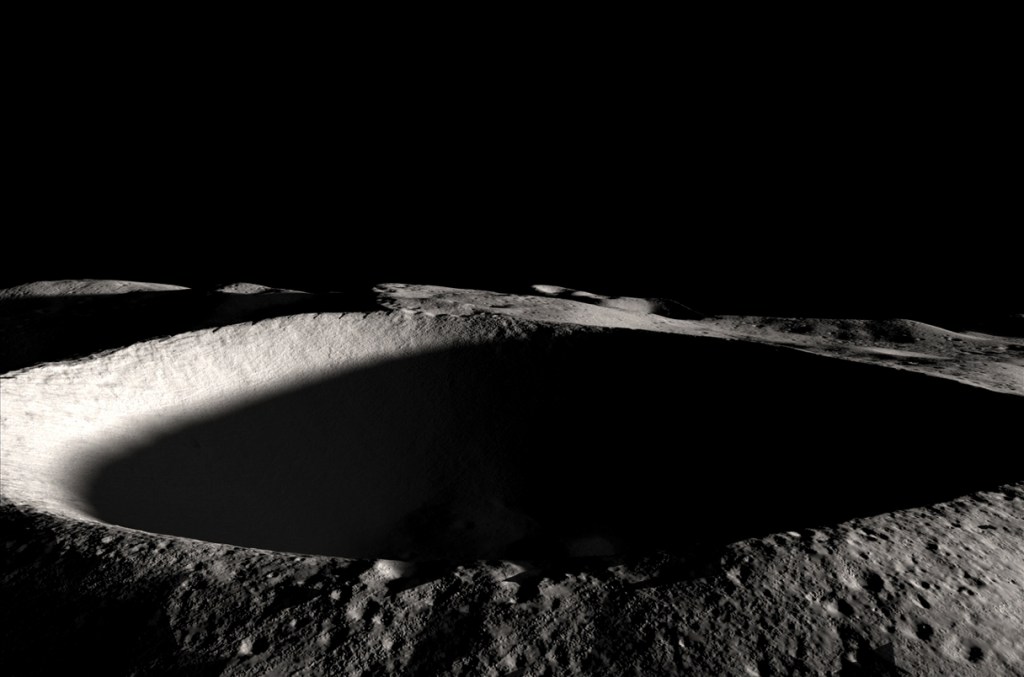

In a significant leap for lunar science and exploration, researchers have unveiled new insights into the moon’s most enigmatic features—its permanently shadowed regions (PSRs). These cold traps, nestled within the lunar poles, are believed to house condensed volatiles, including potentially vast reserves of water ice, which are of paramount importance for both scientific inquiry and…
-
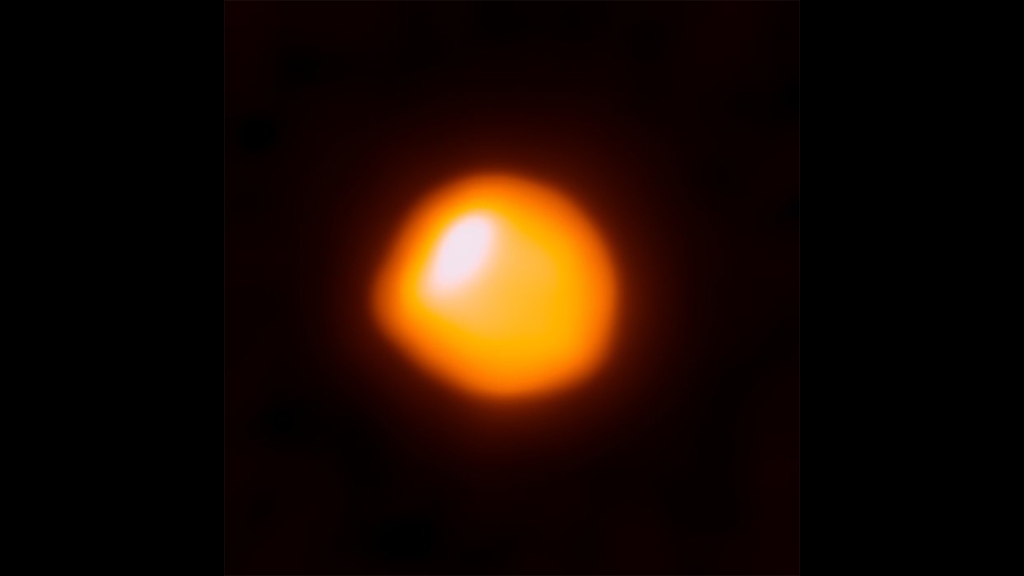

A new study has cast doubts on the prevailing theory that Betelgeuse, one of the closest red supergiants to Earth, is rapidly rotating. Recent observations from the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) showing a dipolar velocity field on Betelgeuse’s surface had led scientists to infer a rotation rate significantly higher than what single-star evolution models…
-
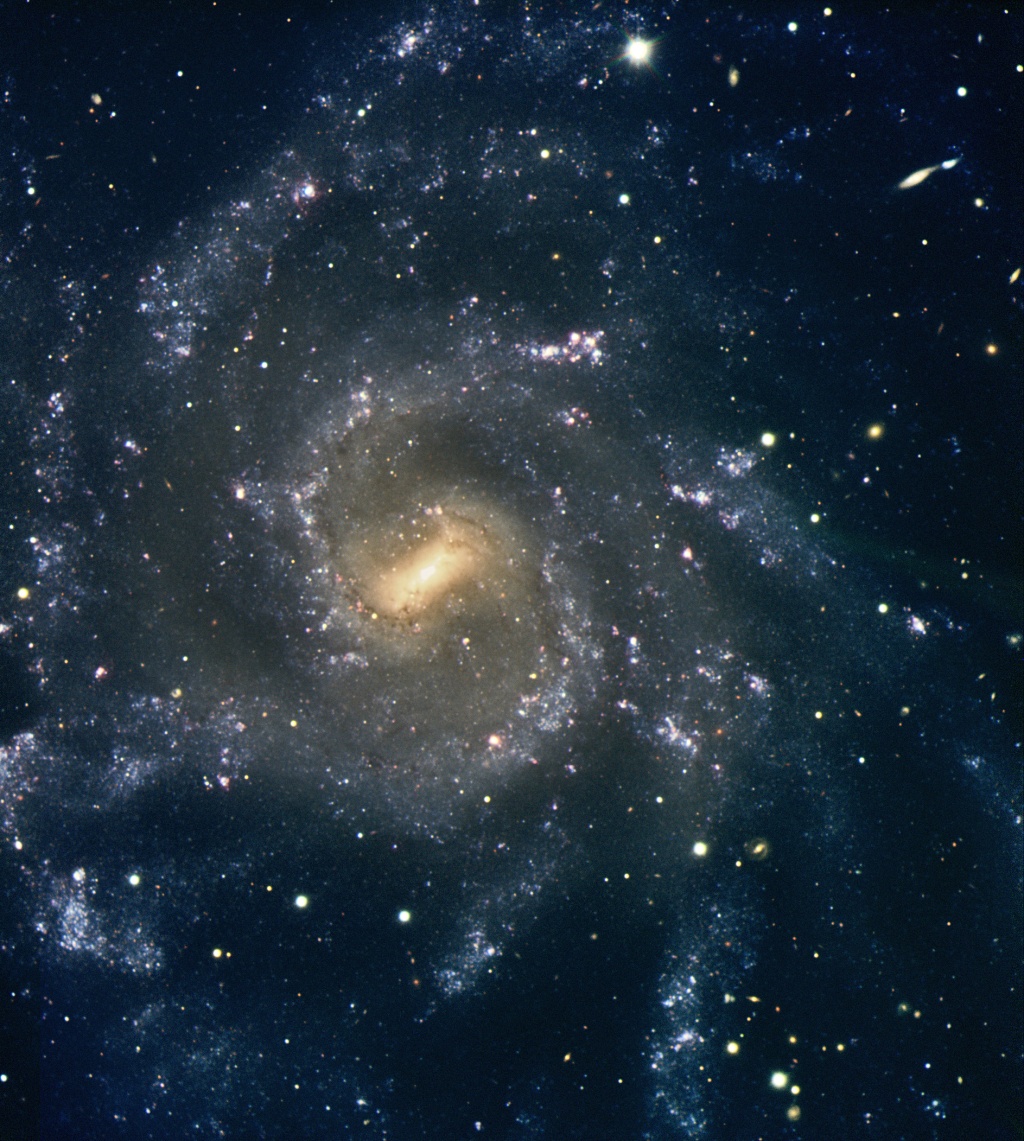

In a recent study focusing on the spiral galaxy NGC 7424, astronomers have made significant discoveries regarding two ultraluminous X-ray sources, designated as 2CXO J225728.9−410211 (X-1) and 2CXO J225724.7−410343 (X-2). These sources have exhibited X-ray luminosities reaching 10,000 times the total power output of the Sun, challenging existing theories of stellar accretion and evolution.
-
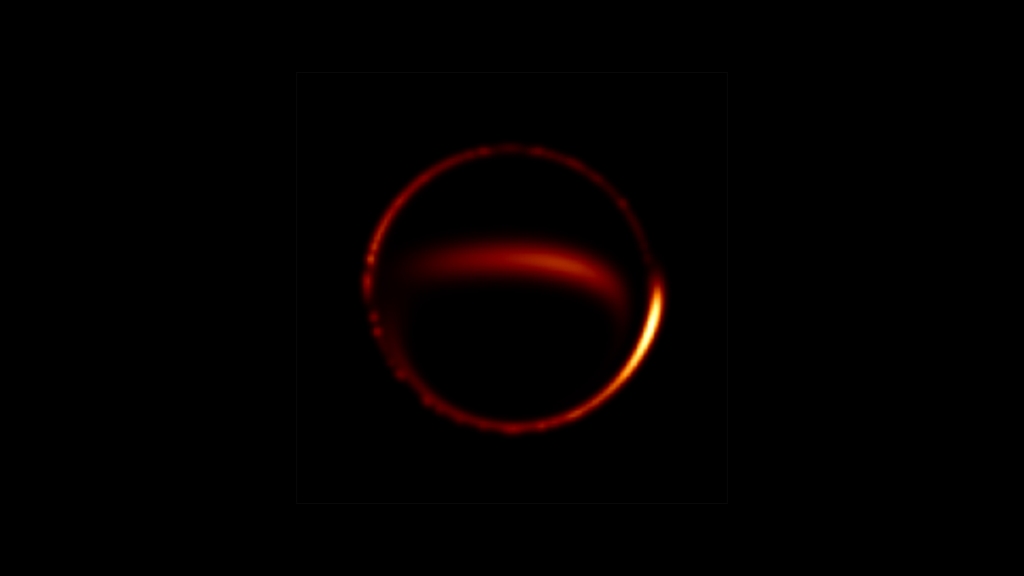

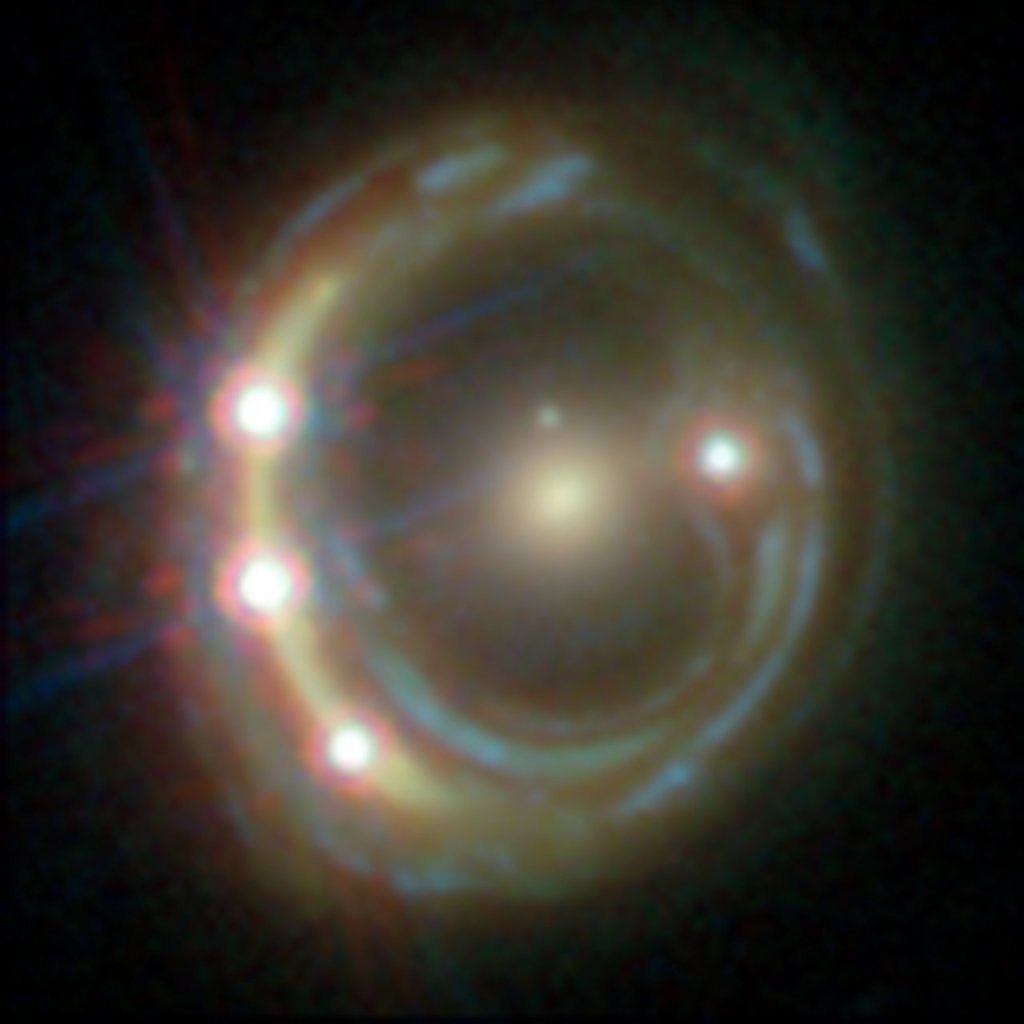
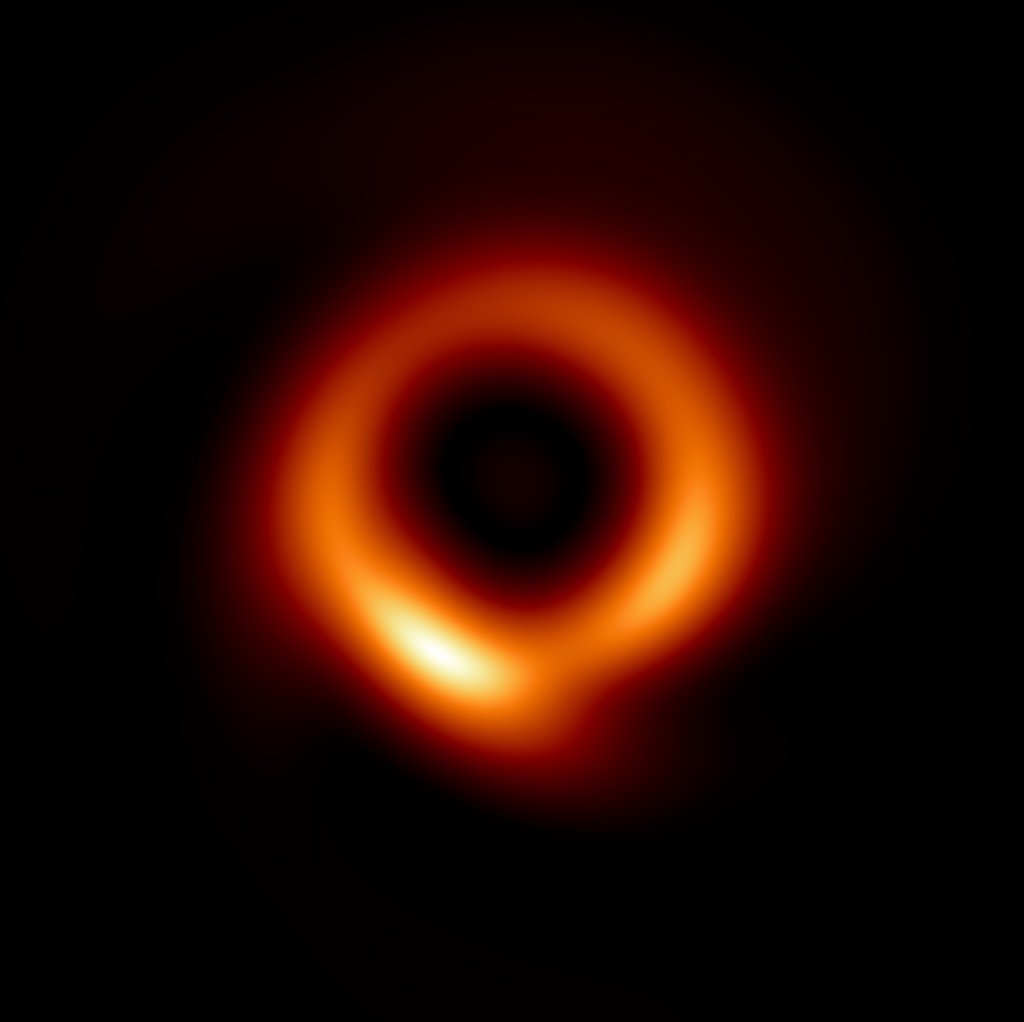
In an era where the imaging of black hole shadows through the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) has captivated the scientific community, a recent study has delved deeper into the phenomena of gravitational microlensing and its implications on these cosmic portraits. Researchers have meticulously analyzed how the gravitational field of intervening compact objects can distort the…
-
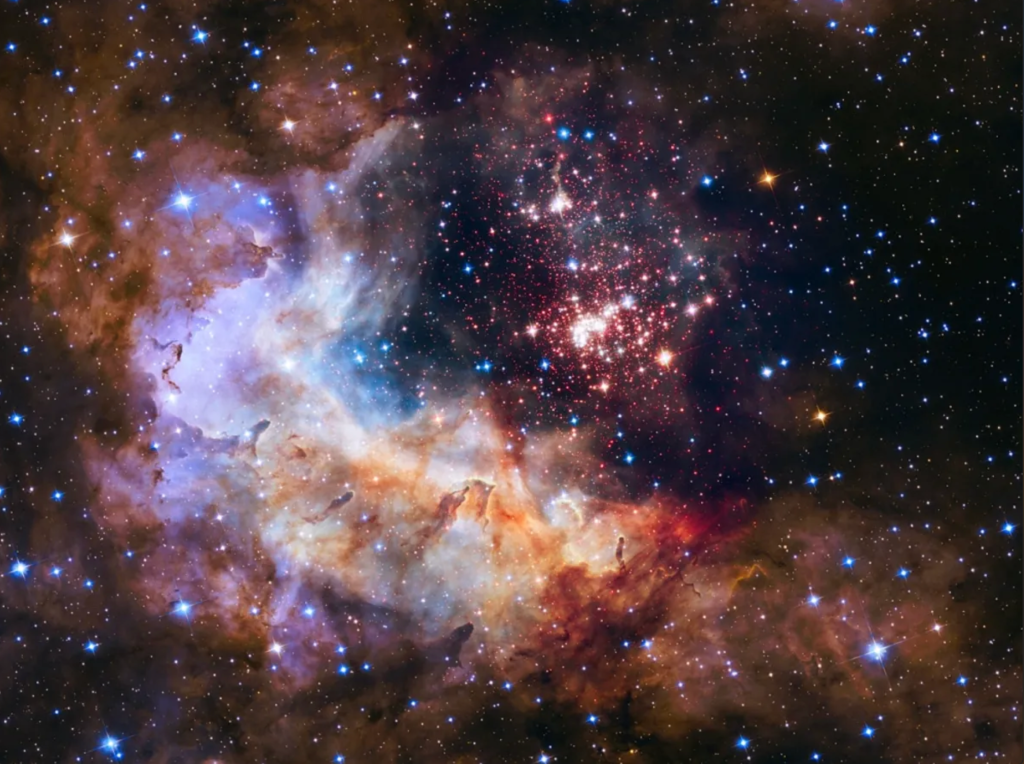

In an ambitious effort to deepen our understanding of the cosmos, astronomers have undertaken a detailed multiwavelength study of NGC 2316, a star cluster nestled within the Milky Way. This research endeavor has provided unprecedented insights into the cluster’s physical attributes and its significant role within the galactic framework.
-
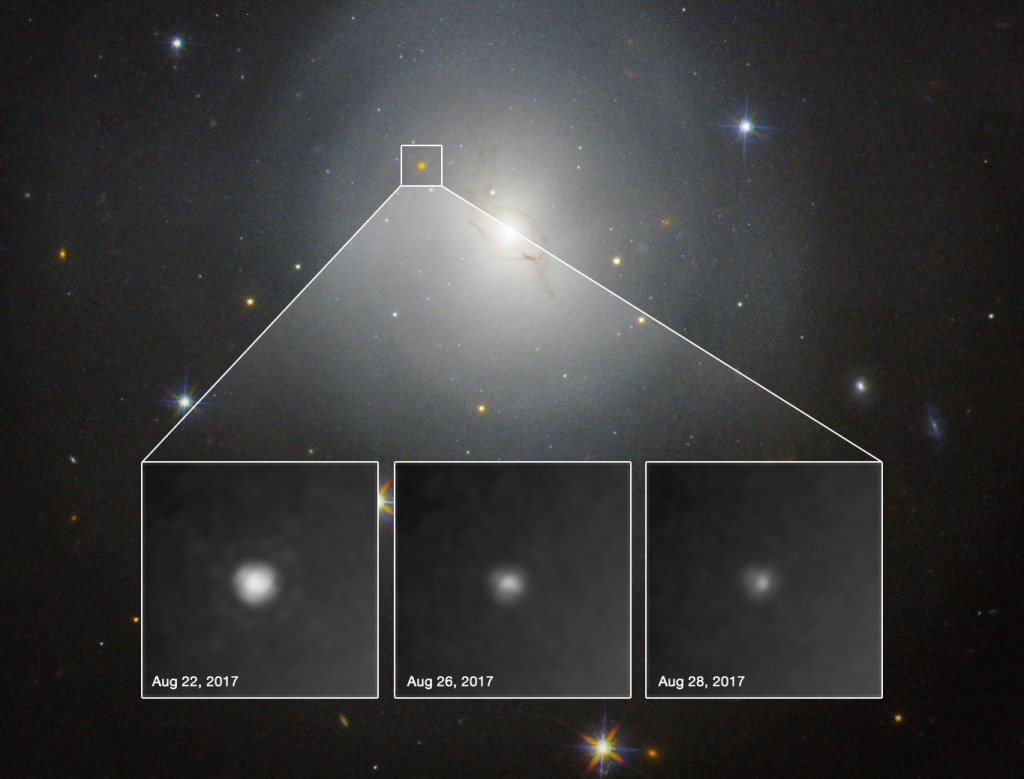

Recent research has revealed isotopes 60Fe and 244Pu in 3 to 4 million-year-old ocean sediments, offering insights into a longstanding cosmic mystery. These discoveries challenge traditional beliefs regarding the cosmic origins of these elements, previously attributed to supernovae and neutron star mergers.
-
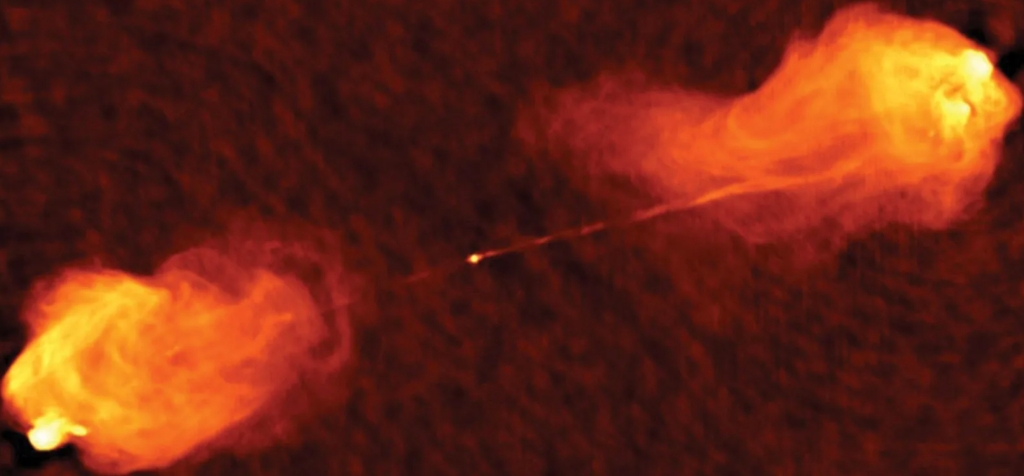
In a new study, astronomers have unveiled the discovery of the most distant heavily obscured, radio-loud active galactic nucleus (AGN) candidate to date, identified in the COSMOS-Web field using a combination of James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) NIRCam/MIRI imaging, mid-infrared, submillimeter, and radio data.
-
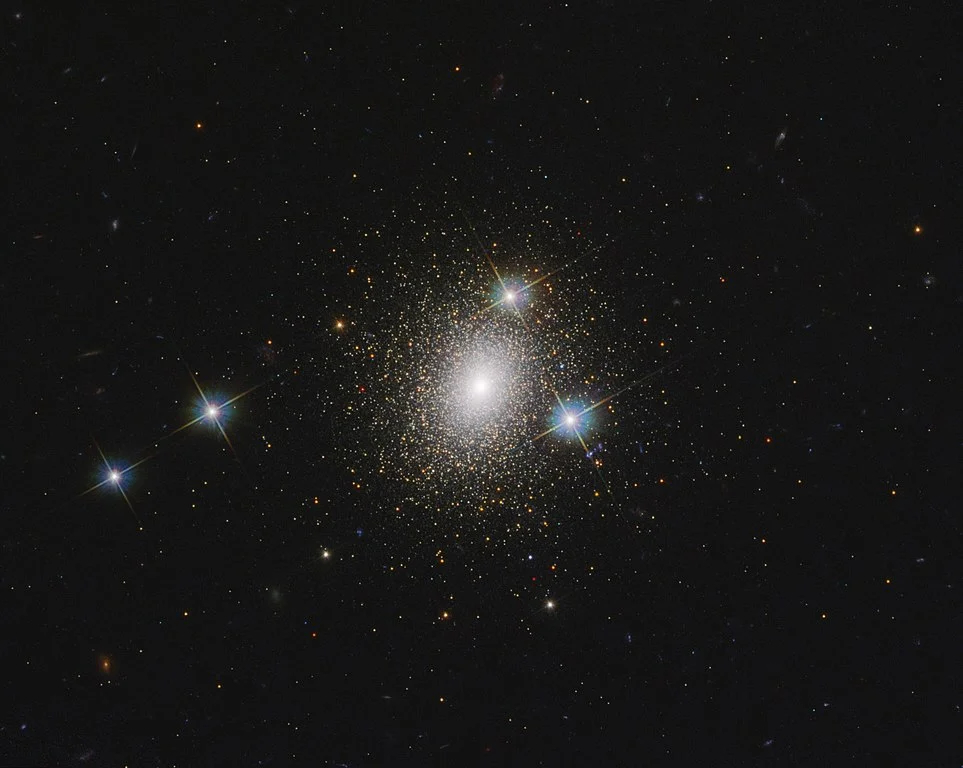

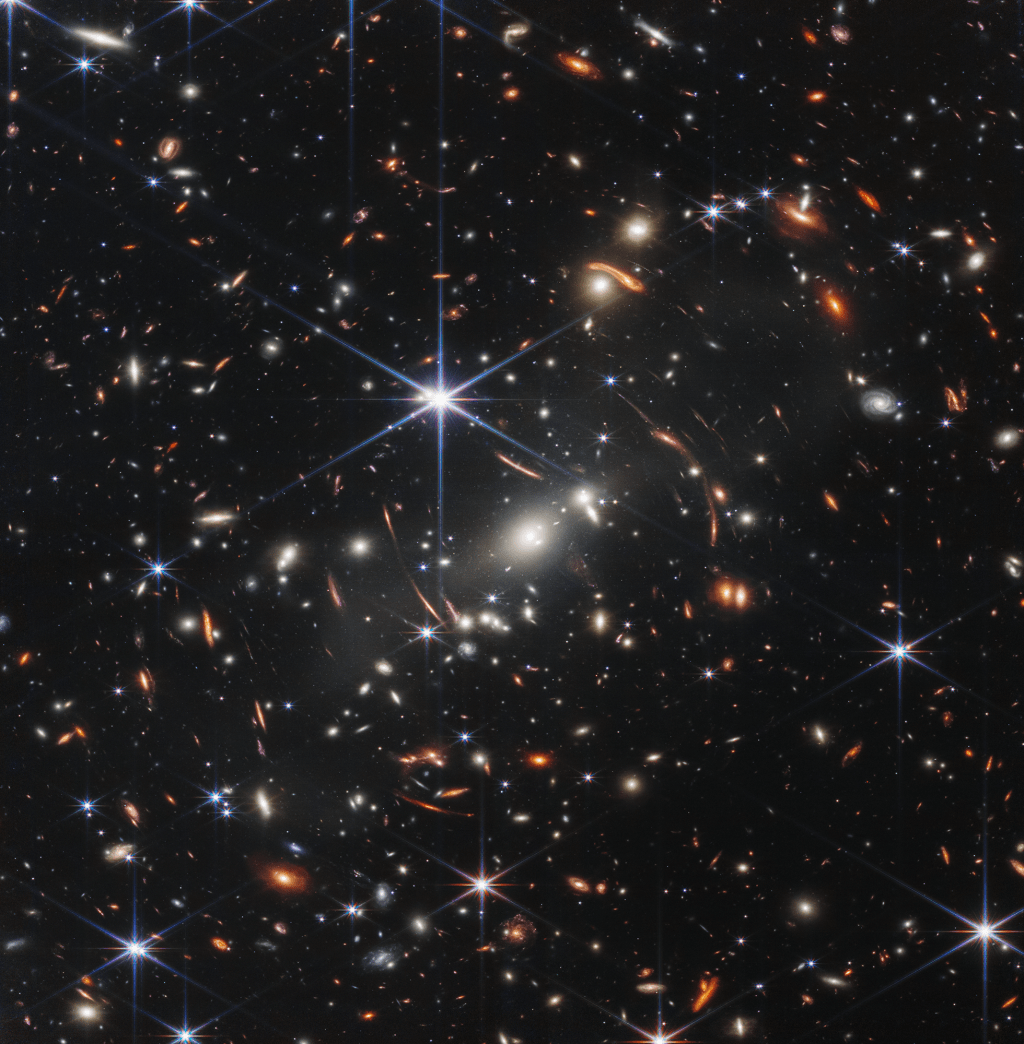
In a groundbreaking advancement in the field of astronomy, scientists have unveiled new catalogs of potential globular clusters (GCs) in 17 nearby spiral galaxies, as part of the extensive PHANGS Hubble Space Telescope (HST) Treasury Survey. These galaxies were meticulously observed across five broadband filters, ranging from the near-ultraviolet to the I band, paving the…
-
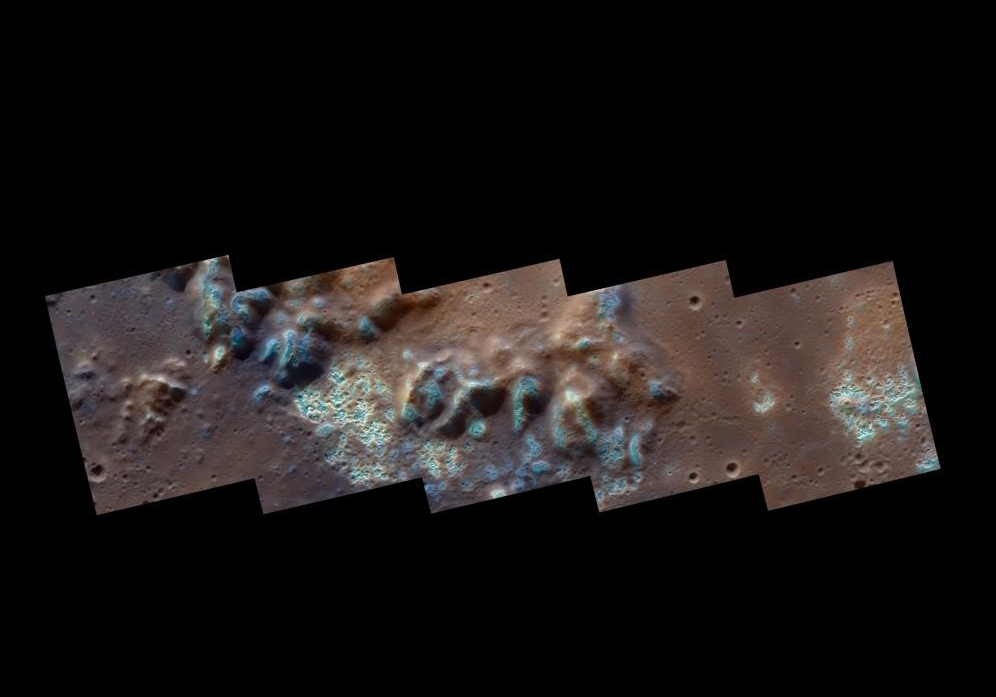

In a new shift in our understanding of Mercury’s geology, recent discoveries have unveiled the planet’s surface to be rich in volatile elements, challenging long-standing beliefs about its composition. Scientists have identified extensive volatile-rich layers (VRLs) beneath Mercury’s crust, potentially stretching several kilometers deep, contradicting the previously assumed volatile-devoid nature of the planet.
-
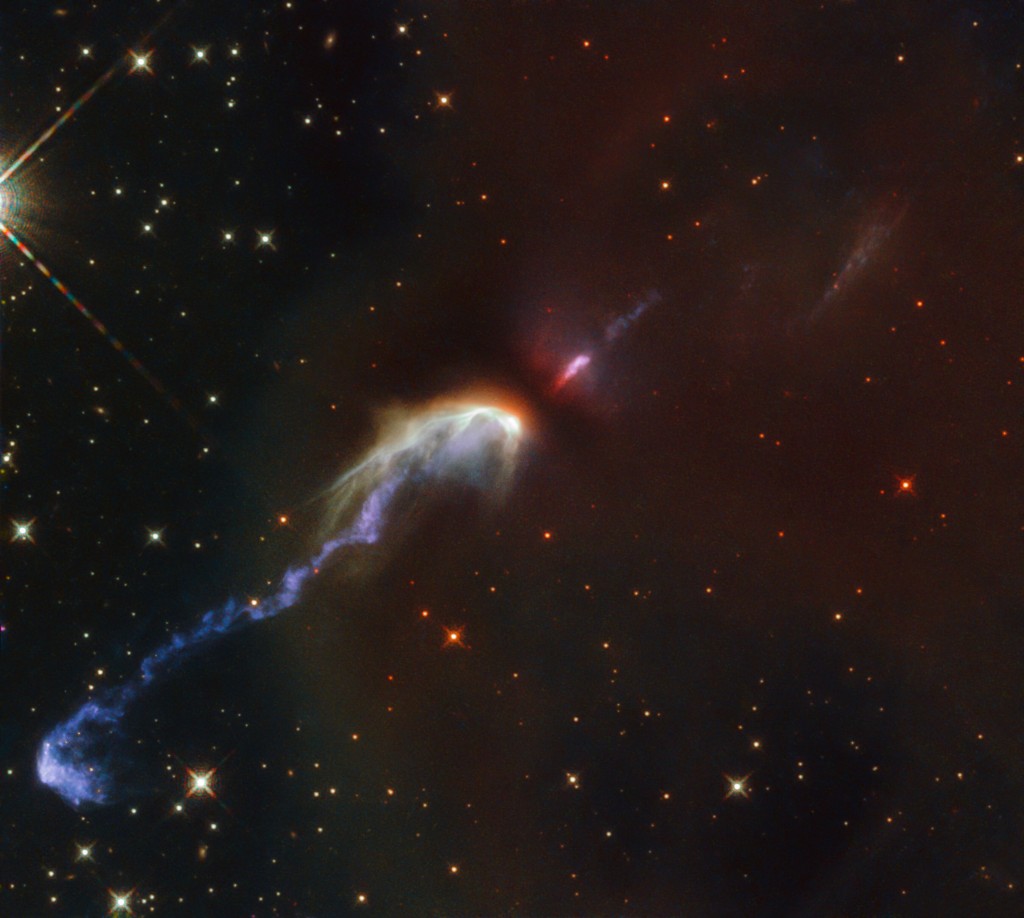

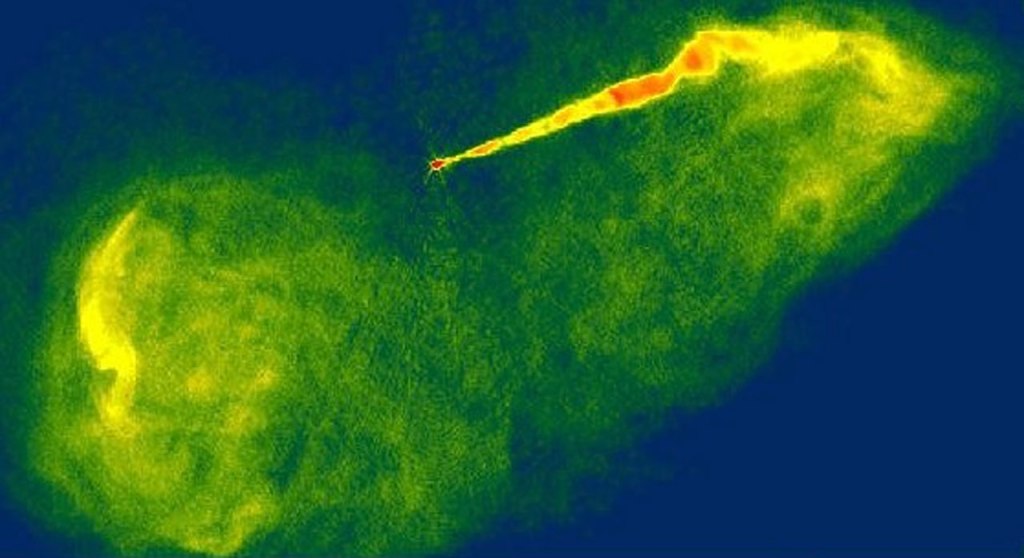
In a new study made possible by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), astronomers have unveiled a highly collimated atomic jet emanating from IRAS 16253−2429, a Class 0 protostar and the dimmest object within the Investigating Protostellar Accretion (IPA) program. This young, deeply embedded star, which has a luminosity of just 0.2 solar masses and…
-

In a new study, scientists have deepened our understanding of the enigmatic rings surrounding Chariklo, the largest known Centaur—a small body orbiting between Jupiter and Neptune. With a diameter of approximately 250 km, Chariklo was discovered to possess two thin rings, marking the first discovery of its kind outside the giant planets. These findings, initially…
-
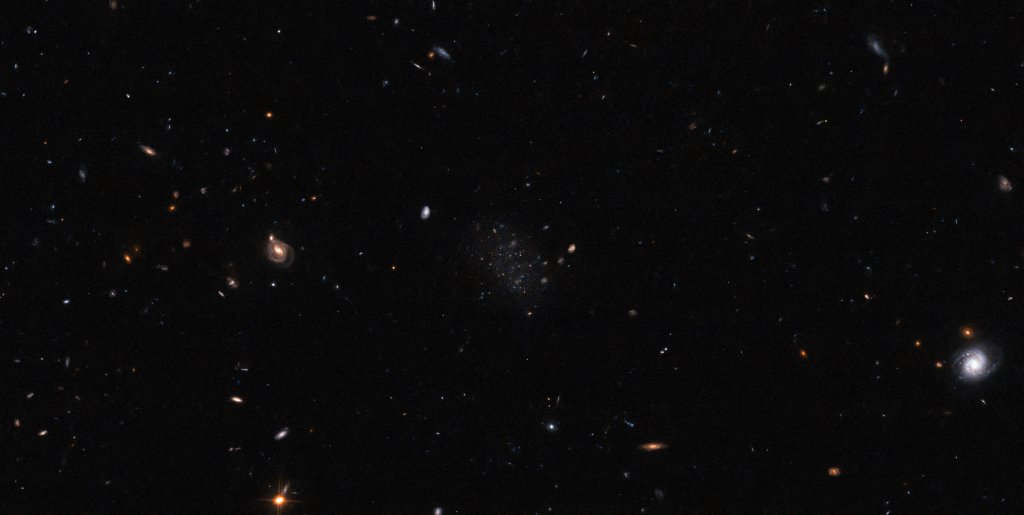

Recent astronomical research has sparked a discussion within the scientific community about the existence of extended stellar halos in ultrafaint dwarf galaxies. Notably, the outskirts of dwarf galaxies in the Local Group have unveiled stars that suggest the presence of these halos. This discovery is pivotal, considering the prevailing notion that such structures were predominantly…
-
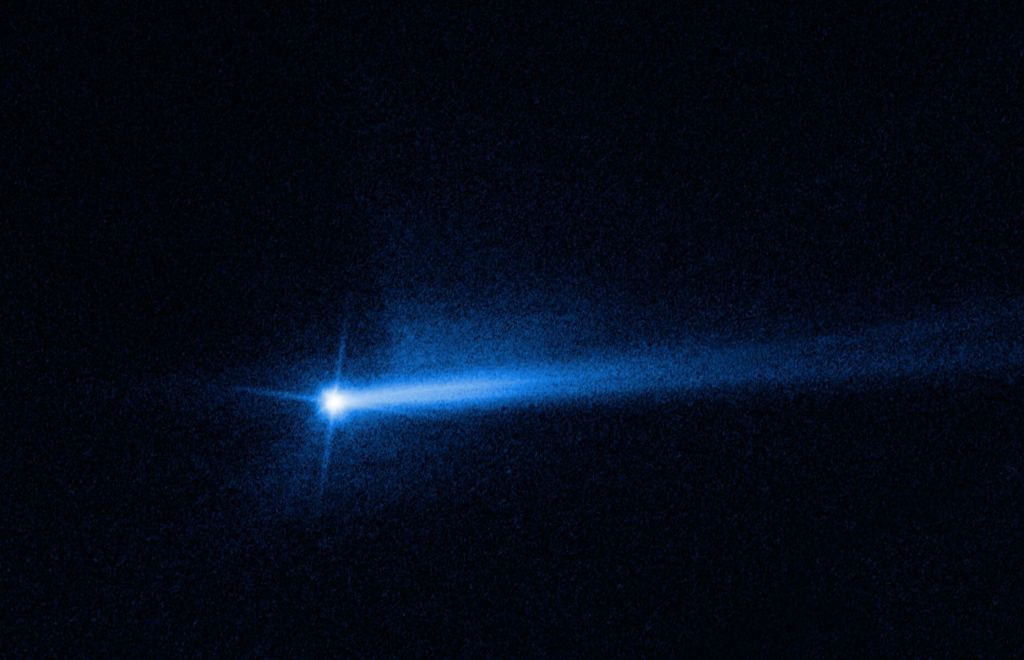

In a recently published study, an updated shape model of the asteroid Dimorphos has been unveiled, shedding new light on its structure and potential changes following the historic Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) mission. The DART mission, a pioneering endeavor by NASA, marked humanity’s first active attempt at planetary defense. On September 26, 2022, the…
-
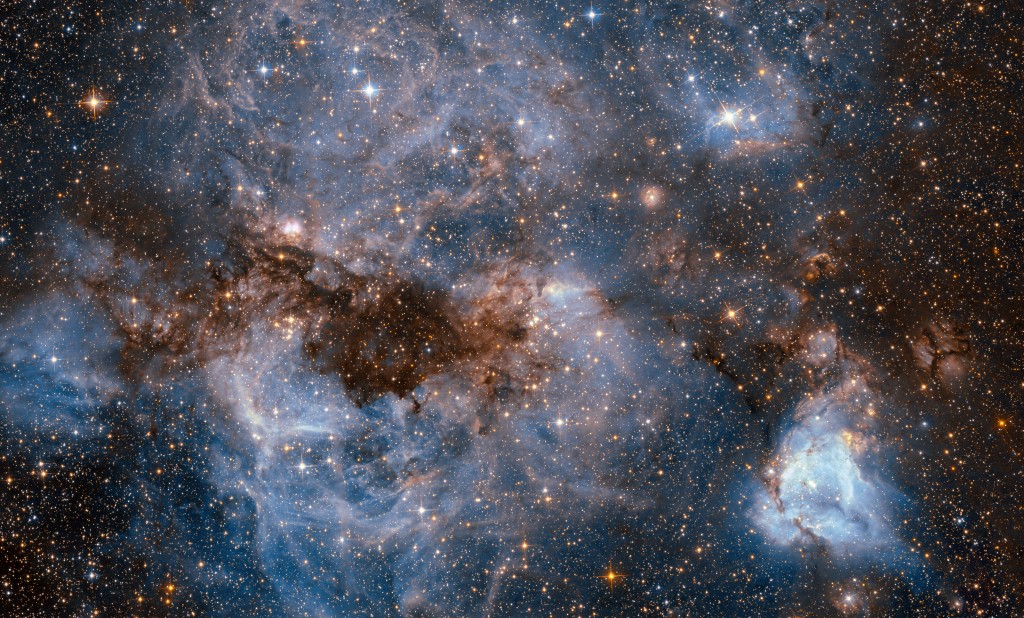

In a new study utilizing Gaia Data Release 3 among other spectroscopic surveys, astronomers have identified 519 high-velocity stars (HiVels) traversing the Milky Way at speeds exceeding 70% of the local escape velocity. These stars, predominantly metal-poor late-type giants, exhibit complex trajectories and origins. Notably, nine of these stars are prime candidates for escaping the…
-
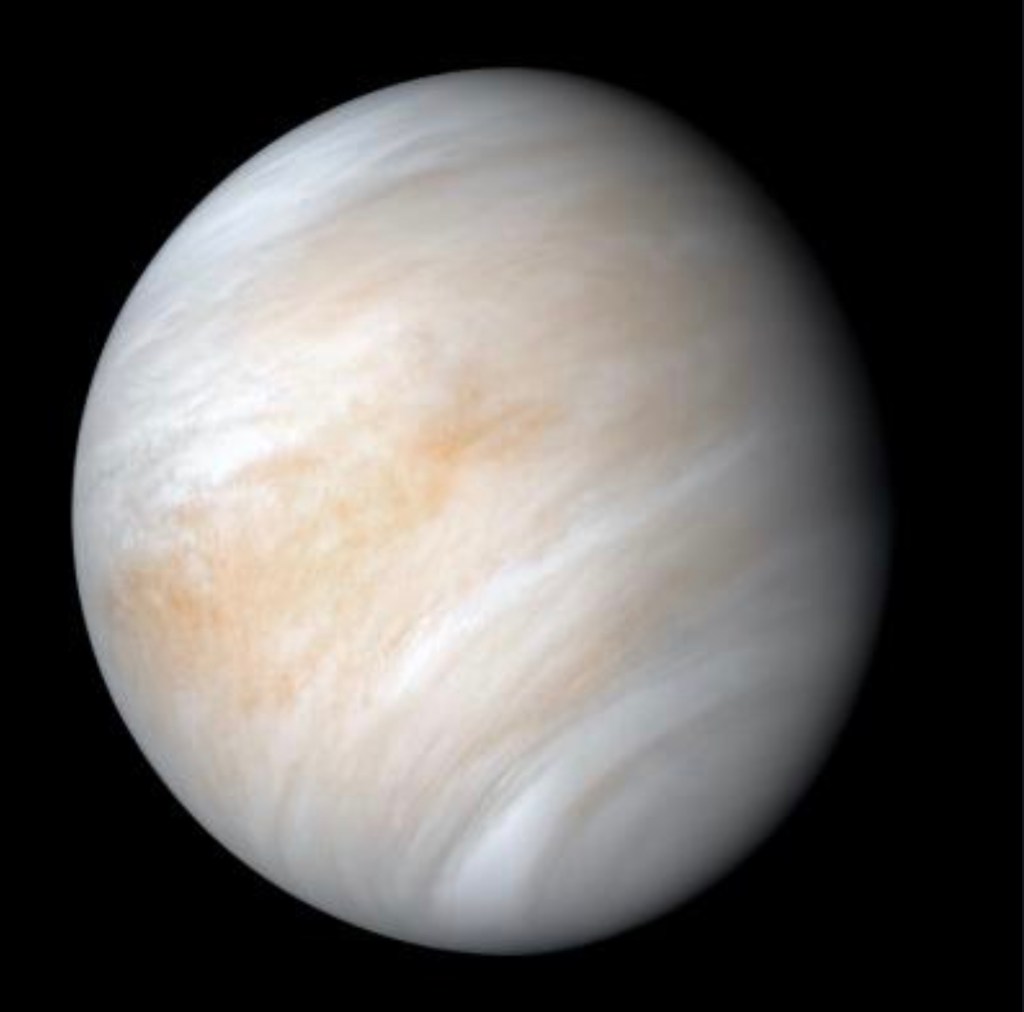

Researchers have made significant advancements in understanding the interactions between the solar wind and planetary atmospheres, specifically focusing on Venus. The solar wind, a stream of charged particles ejected from the sun, forms a magnetic barrier when it encounters a planet. This barrier is where magnetic pressure surpasses the plasma pressure, a phenomenon particularly observed…
-
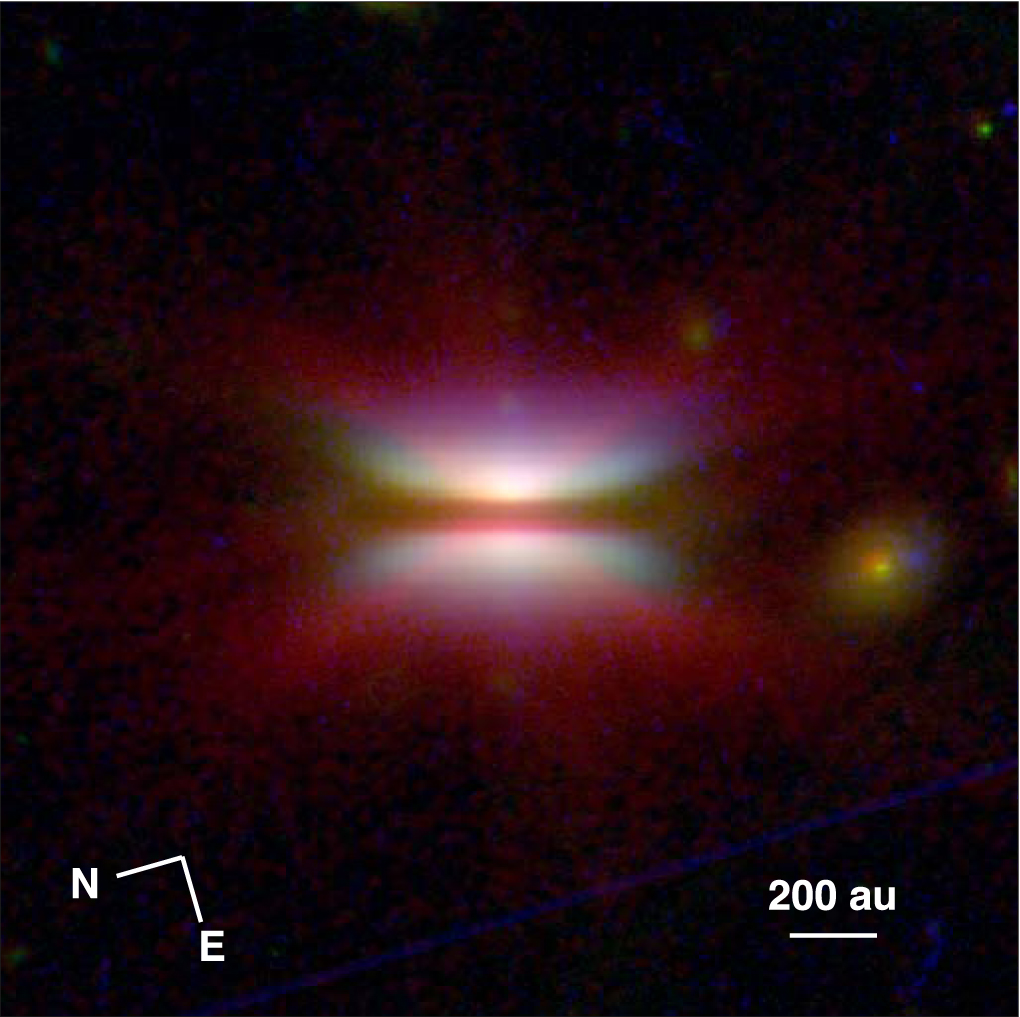
In an exciting development, the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has provided groundbreaking images of a protoplanetary disk surrounding a young star. These observations mark the longest wavelengths at which a protoplanetary disk has been resolved in scattered light, offering unprecedented insights into the disk’s geometry and properties.
-
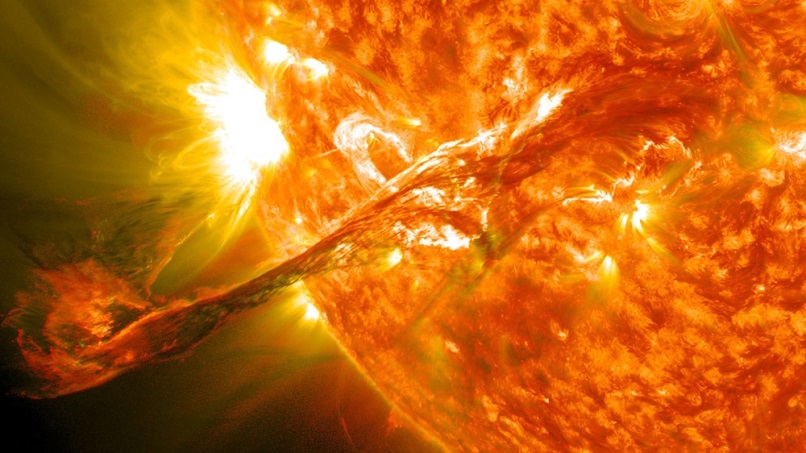

A recent study conducted using the Chinese Hα Solar Explorer (CHASE) has made significant strides in decoding the complex three-dimensional movements of solar filaments, a key factor in predicting space weather phenomena. These solar filaments, also known as prominences when observed on the edge of the Sun, eject massive amounts of plasma and high-energy particles…
-
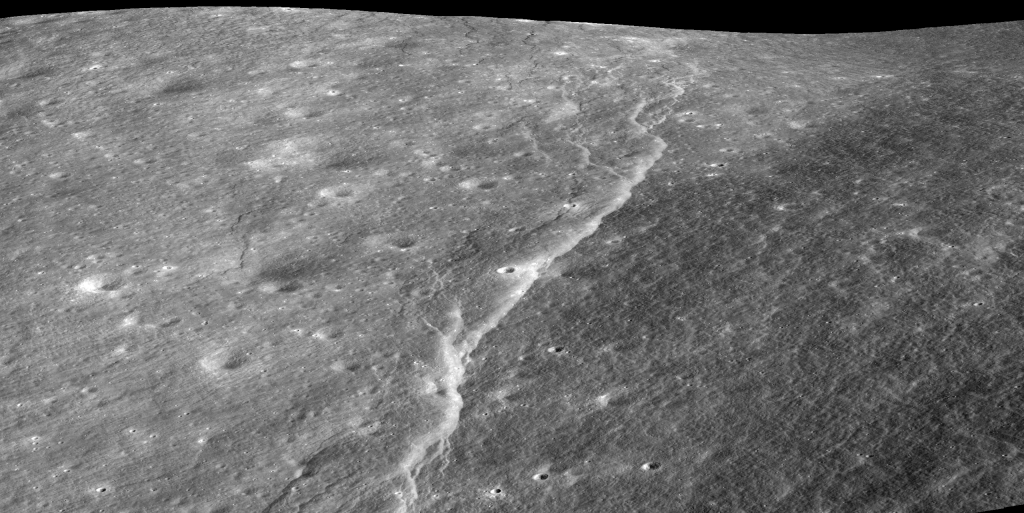

A recent study has cast a spotlight on the dynamic tectonic landscape of the Moon’s south pole, revealing a series of features pointing to ongoing seismic activity. Notably, the de Gerlache Rim 2 region, a candidate landing site for the Artemis III mission, is home to a cluster of these scarps, underscoring the need for…
-
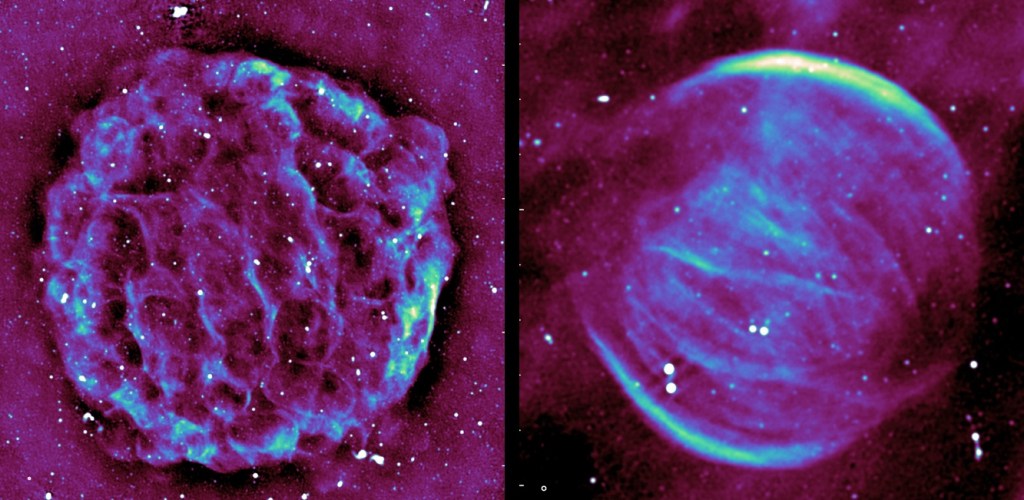
In a new study, astronomers have utilized the MeerKAT radio observatory to investigate 36 supernova remnants (SNRs) across a specific frequency range. The observations unveiled detailed, high-dynamic-range images brimming with intricate structures, marking a significant advancement in our understanding of these celestial phenomena.
-
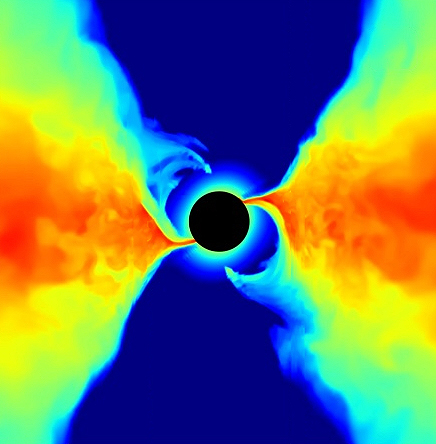
In a new study, astrophysicists have delved deep into the enigmatic realm of neutron stars and black holes in X-ray binaries, known for their powerful and focused jets during specific spectral states. Recent strides in computational astrophysics have allowed researchers to utilize numerical simulations to unravel the complexities behind jet formation and its characteristics.
-
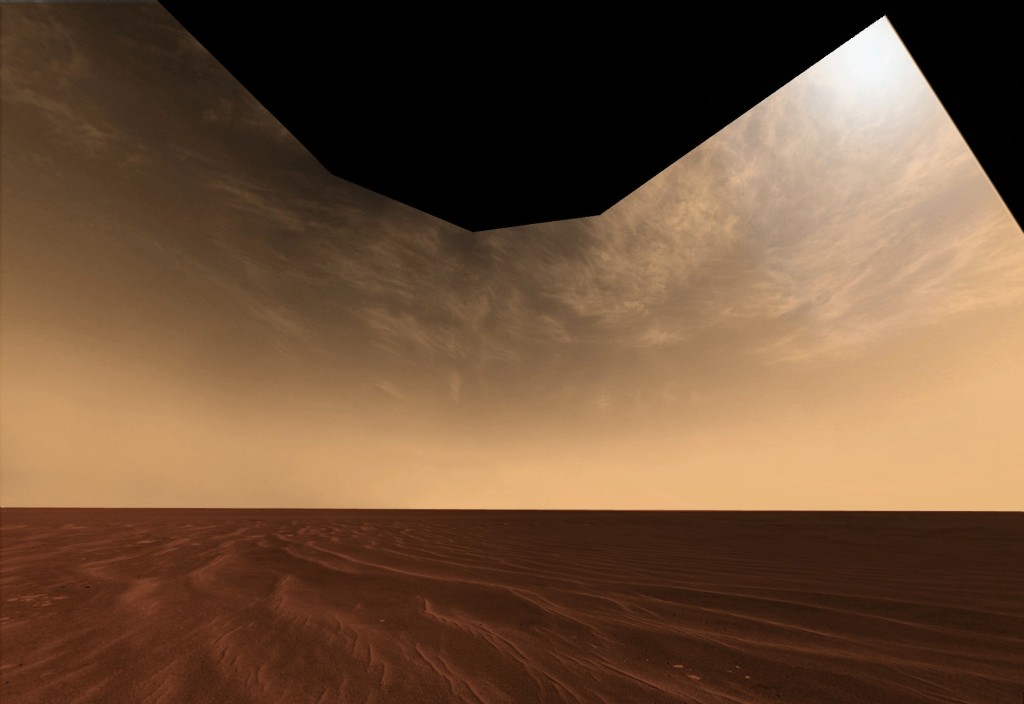

In a new study looking to unravel the atmospheric secrets of Mars, the Perseverance Rover has presented unprecedented data from its extensive study of cloud formations above Jezero Crater. Over the first 600 sols, the mission meticulously gathered 46 cloud movies and 145 cloud surveys, showcasing an array of cloud types and behaviors at the…
-
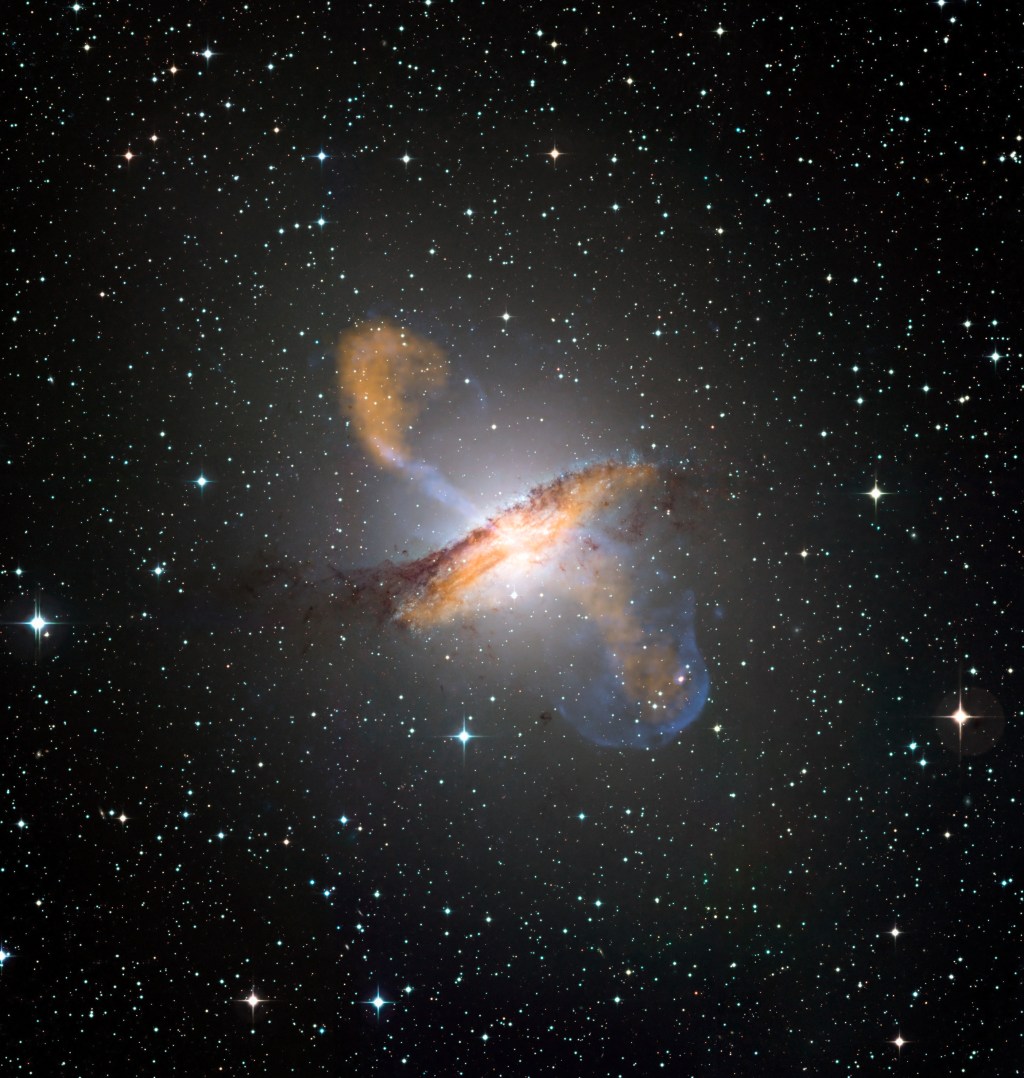

In a recent astronomical breakthrough, scientists have discovered an exceptionally obscured, radio-loud active galactic nucleus (AGN) candidate, marking the highest redshift observed in such a category. Utilizing the unparalleled capabilities of the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) combined with multifrequency radio observations and mid-IR photometry, researchers have identified a massive supermassive black hole (SMBH) in…
-

Quasars, or quasi-stellar objects, are some of the most luminous and enigmatic objects in the universe, offering a window into the early epochs of cosmic evolution and the mechanics of supermassive black holes. These celestial phenomena challenge our understanding of physics under extreme conditions and play a critical role in the study of galaxy formation…
-
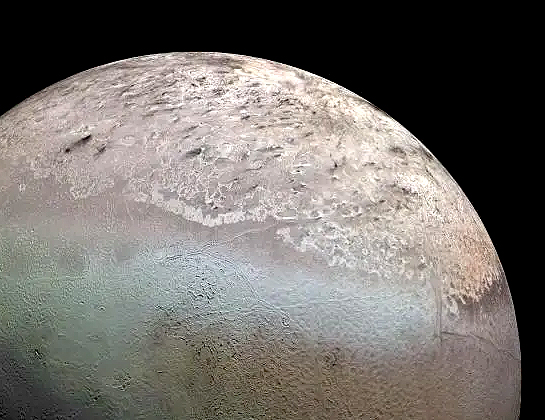

Neptune’s moon Triton stands as one of the most intriguing and enigmatic bodies in our solar system. Discovered in 1846 by British astronomer William Lassell, just 17 days after Neptune itself was identified, Triton is unique among the large moons of the solar system for its retrograde orbit – an orbit opposite to the planet’s…
-
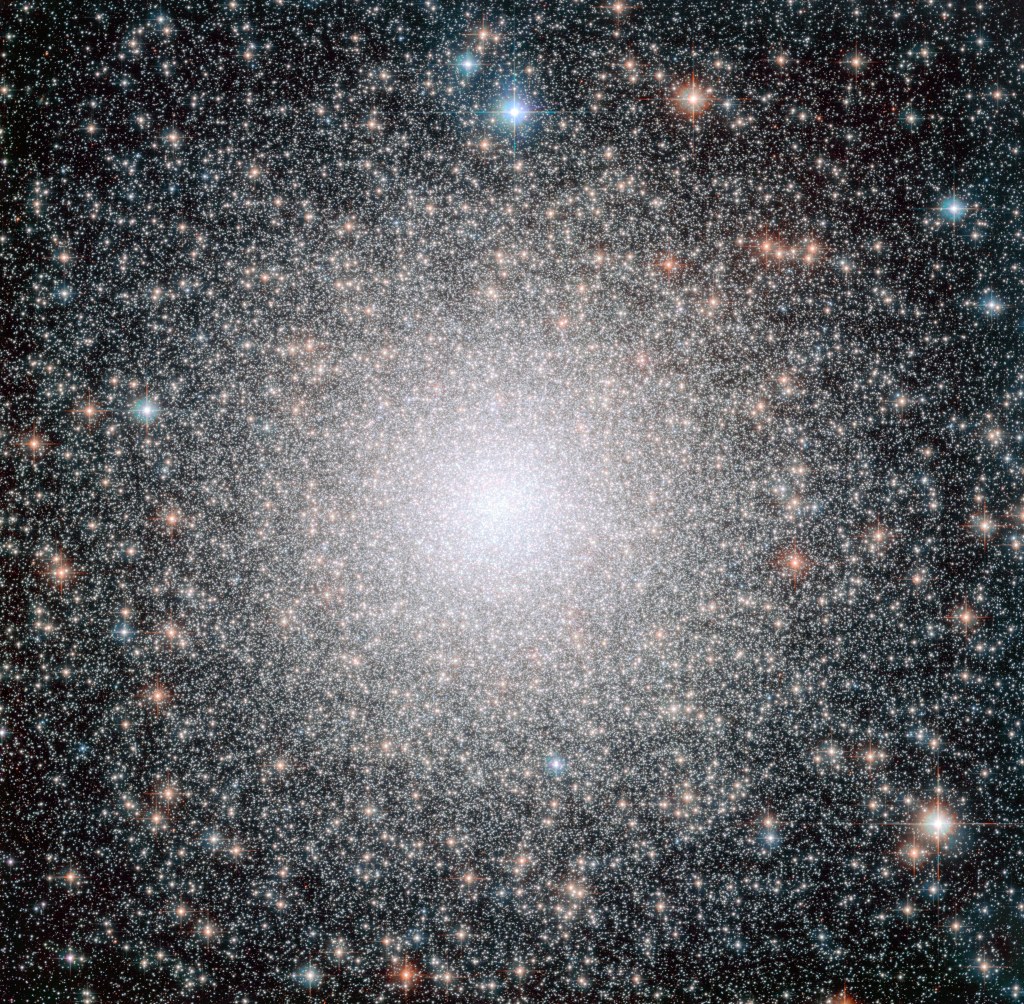

Globular clusters, some of the oldest and most intriguing objects in the cosmos, have captivated astronomers and space enthusiasts for centuries. These spherical collections of stars are not just spectacular to behold but are also crucial in deepening our understanding of galaxy evolution, dark matter, and the universe’s history.
-

Gravitational waves, a profound concept in astrophysics, have become instrumental in our understanding of the universe. Their discovery and ongoing study offer a new lens through which we can observe and comprehend cosmic events and the very fabric of spacetime. This essay explores the nature of gravitational waves, their detection, and their significance in enhancing…
Bringing you news about the universe down to earth daily
Proudly Powered by WordPress